Torrefaction of Briquettes Made of Palm Kernel Shell with Mixture of Starch and Water as Binder
Keywords:
Palm kernel shell, starch binder, torrefaction, briquette, temperature effect, flow rate effectAbstract
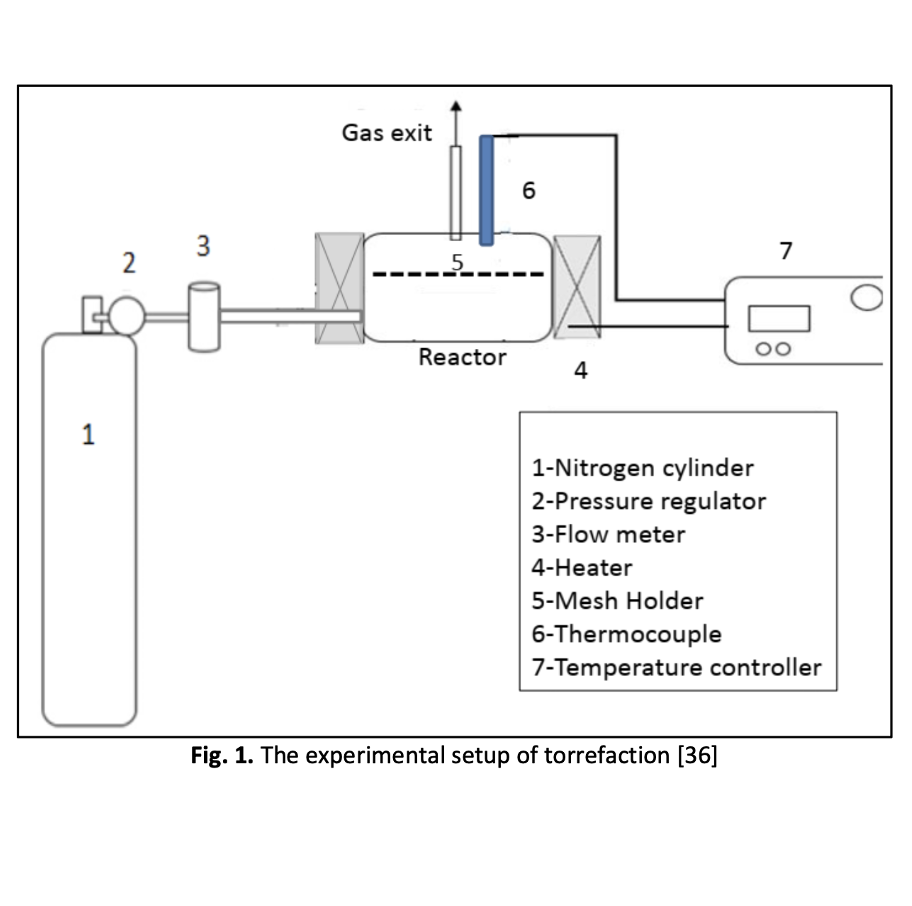
This study presents physical and combustion properties of briquettes made of palm kernel shell (PKS) with mixture of starch and water as binder. The briquettes with weight ratio of 60:40 (PKS: starch binder) were torrefied at various temperatures (225- 275℃) and nitrogen flow rates (1000-3000 mL/min). The physical properties such as appearance, compressive strength, density and mass yield as well as combustion properties such as high heating value (HHV), energy yield and proximate analysis of untorrefied and torrefied briquettes were determined in the present study. The performances of the torrefied briquettes were also compared with the case of untorrefied briquettes as well as international benchmarks. It was found that torrefaction temperature significantly affects the properties of torrefied briquette rather than volume flow rate of nitrogen. At severe torrefaction condition (temperature of 275℃), HHV of 22.16±0.23 MJ/kg was obtained, that is the highest if compared to HHV of the briquettes torrefied at other temperatures. It was found that properties of the torrefied briquettes do not really affected by nitrogen flow rate. Overall, with the presence of starch binder, briquettes with considerably high compressive strength were obtained if compared to the previously developed binderless PKS briquettes.
Downloads