Saturated Porous Ferroconvection in a Ferrofluid Layer with Viscosity as a Function of Magnetic Field: Focus on Convective Boundary Condition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.115.1.126142Keywords:
Ferroconvection, porous medium layer, Galerkin method, MFD viscosity, paramagnetic boundariesAbstract
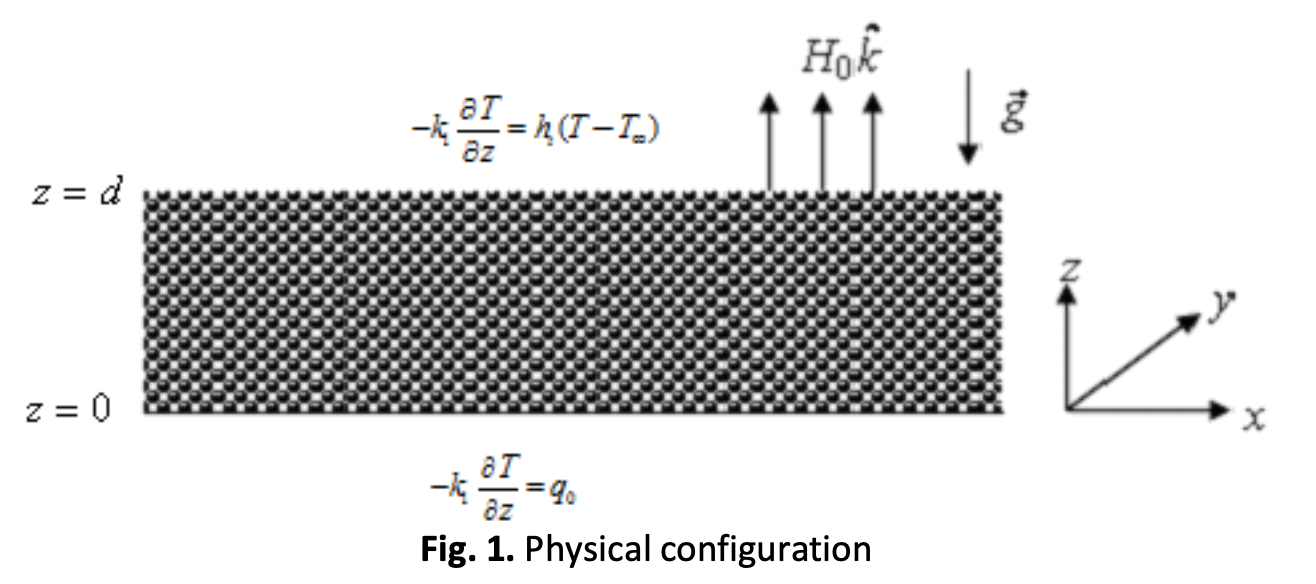
The present work aims to examine the influence of magnetic field dependent (MFD) viscosity on the onset of ferroconvection (FC) in a horizontal porous layer saturated with a quiescent ferrofluid (FF) and subjected to a uniform vertical magnetic field. It is assumed that the porous boundaries at the bottom and top are rigid-paramagnetic. The thermal conditions consist of a constant heat flux at the lower surface and a convective boundary condition at the upper surface, encompassing fixed temperature and uniform heat flux cases. The application of the Galerkin technique to the resulting eigenvalue problem reveals that the stability region expands as the porous parameter, Biot number, MFD viscosity parameter and magnetic susceptibility increase in magnitude. Conversely, the stability region contracts as the magnetic number and non-linearity of magnetization increase. Furthermore, it is noted that under uniform heat flux boundary conditions, the criterion for the initiation of ferroconvection remains unaffected by the non-linearity of fluid magnetization.
Downloads