Impact of Insulation using Bio-sourced Materials on the Thermal and Energy Performance of a Typical Residential Building in Morocco
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.117.1.4359Keywords:
Thermal and energy study, thermal comfort, energy requirements, residential building, TRNSYS software, bio-sourced insulation materialsAbstract
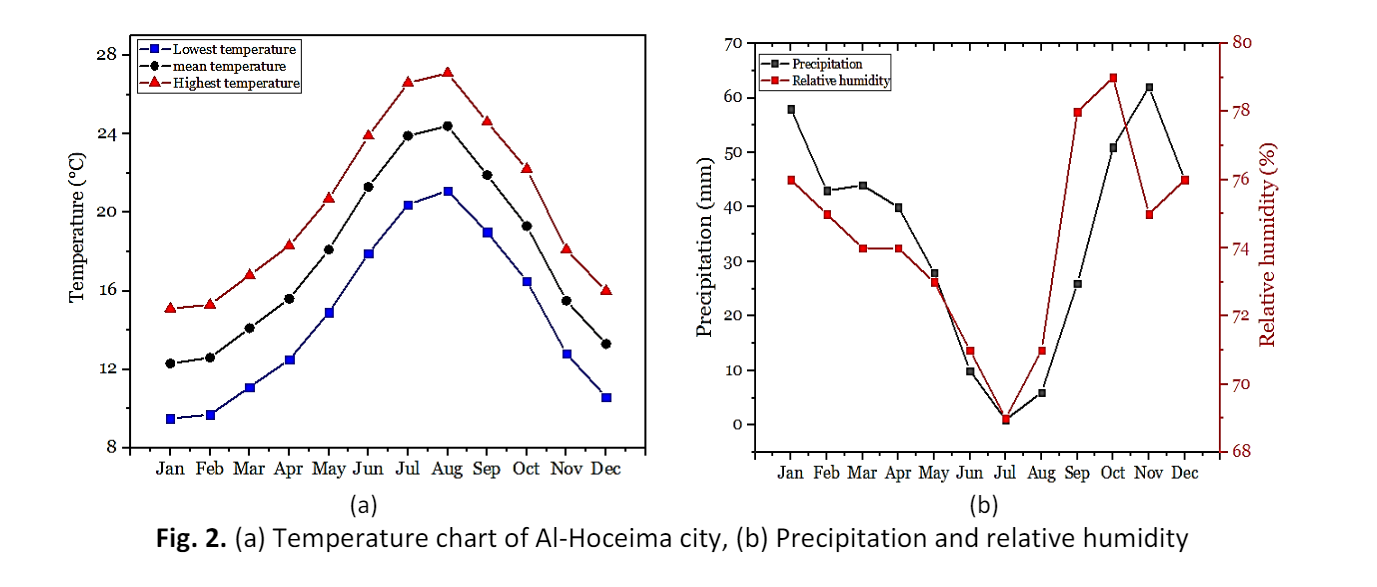
Among the measures to be taken to design and construct buildings with envelopes that are more energy-efficient, sustainable, and environmentally friendly is thermal insulation using a very wide range of insulating materials, either synthetic or of natural origin or derived from biomass. The present work represents a thermal and energy study aimed at improving the thermal comfort levels and energy requirements of a typical residential building located in the city of Al-Hoceima, Morocco. To this end, a series of numerical simulations were carried out using TRNSYS software to assess the impact of applying three bio-based insulation materials, namely hemp wool, wood fiber, and expanded cork, in the wall layer of the building. Different insulation scenarios were studied to make a choice that would ensure optimum comfort in the building with low energy demand. The results of this study show that insulating the roof with 8 cm of hemp wool contributes to energy savings of up to 36.7% and 35.2% for cooling and heating demand respectively. In thermal terms, improvements in the temperature inside the building have been achieved: in January, the maximum temperature recorded is 20.94°C, while in July, the maximum temperature is around 26.80°C.
Downloads