Improving Hasanuddin University Lake Water Quality by Controlling Contamination Sources and Biological Monitoring Systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.114.1.166177Keywords:
Ecosystem protection, infrastructure, research, sustainable practices, wetlandsAbstract
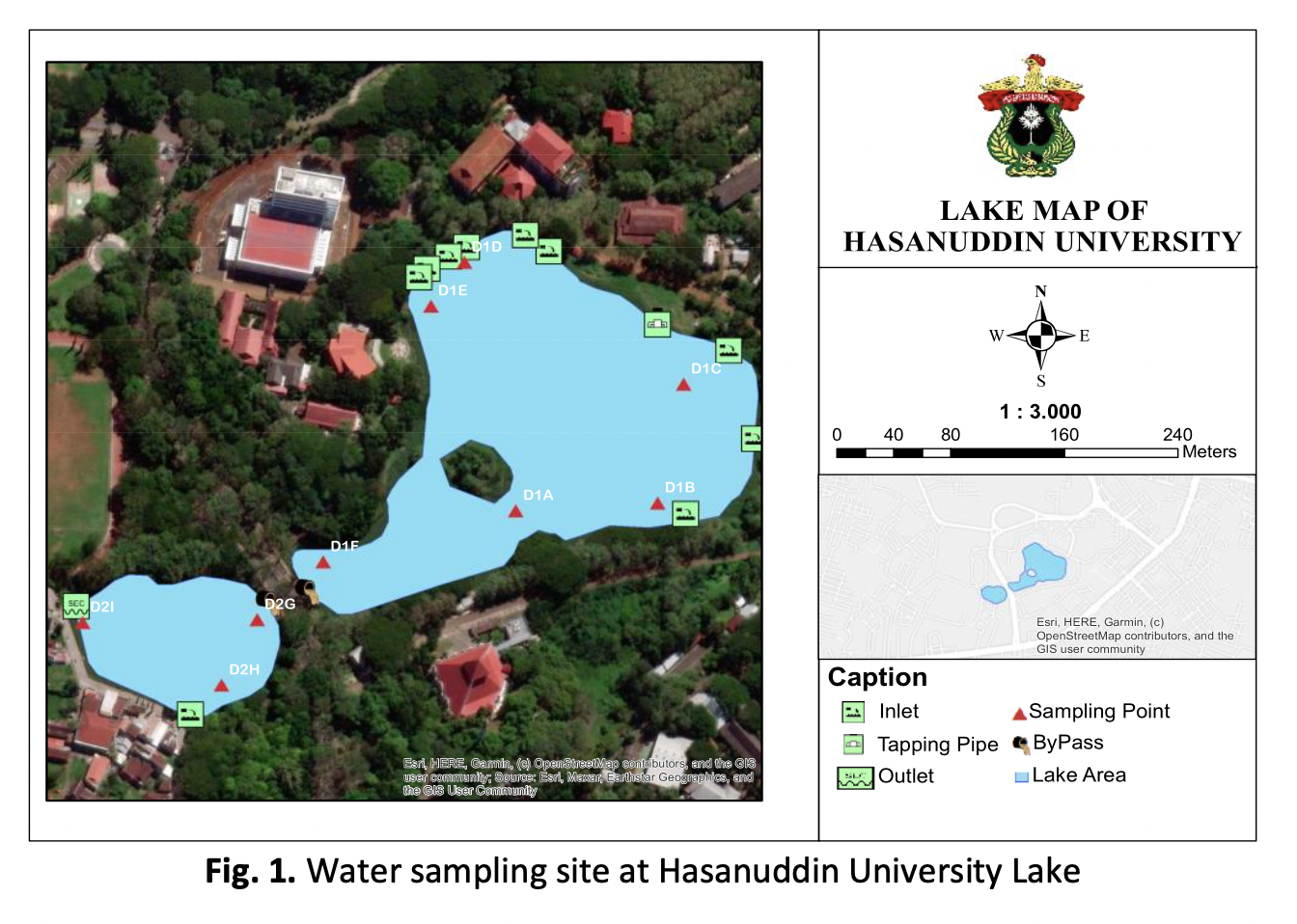
Hasanuddin University Lake in Indonesia is a water tourism destination that offers natural beauty and comfort. In addition, the lake functions as an important scientific development park for the university. Even though its location is on campus, the surroundings of the campus are residential areas and various life activities. Recently, weed growth has occurred, which could be an indication of contamination and may hinder its useful function. Therefore, this study investigates the physicochemical quality of water, the pollution index, and its monitoring, attempting to make the campus lake continue to function sustainably. The research was carried out at the peak of the dry and rainy seasons, with laboratory examinations based on standard methods for quality parameters that follow lake use function standards. The results showed that most of the water quality parameters measured needed to meet the required quality standards. Based on the scoring results using the water pollution index method, lake water is classified as lightly to moderately polluted, which requires protection. The monitoring method is prepared with the addition of a biological indicator system. In line with that, intensification of the diversity of greenery around the lake and environmental management in an integrated manner with the surrounding settlement. The conclusion is that there is a need for complementary monitoring between physicochemical and biological methods and management coordination with the surrounding territories.
Downloads