Determination of Thermal Conductivity Constant for Spray-Dried Mung Bean Protein Isolate using Series-Parallel “Block” Method and Central Composite Design
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.114.2.155164Keywords:
Mung bean protein isolate, optimization, central composite design, series-parallel combinationAbstract
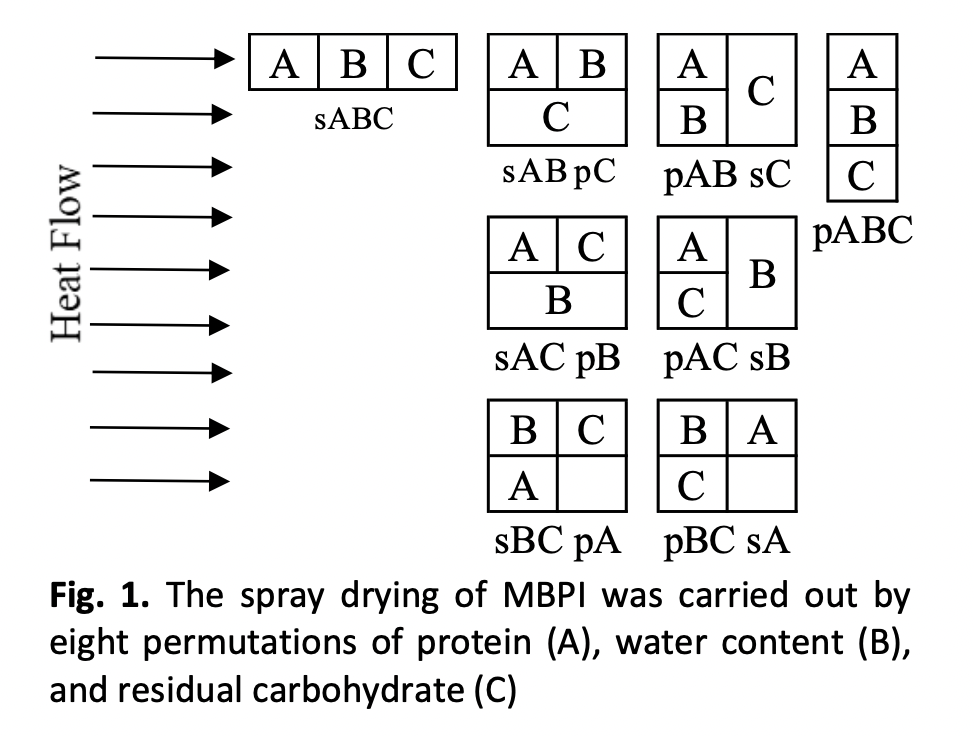
The efficient production of mung bean protein isolate (MBPI) is essential for sustainable food processing, yet it is energy-intensive due to drying phase required to convert raw mung beans into a fine powder. This work was carried out to calculate the thermal conductivity constant (k) of protein (A), moisture (B) and residual carbohydrate (C) of spray-dried MBPI. The protein slurry was prepared by dissolving MBPI in water at the ratio of 1:3, 1:4, and 1:5 prior to spray drying. The protein slurry was then spray dried at three different inflow temperatures of 140, 160, and 180 °C. A Series and Parallel Combination "Block" Model in tandem with a Central Composite Design (CCD) were selected to calculate the thermal conductivity constant of A, B and C. Eight arrangement components on A, B, and C component, measurements were derived from the initial three data points by utilizing the CCD method, in the preliminary study. By utilizing the series-parallel approach and statistical combination, there are a total of forty study arrangements. The thermal conductivity of MBPI with arrangements of A, B, and C (pABC); and a series of combinations of A and C in parallel to B (sAC pB) ranged from 0.1964-0.224 Wm-1 ℃ -1, with R2 = 98.73%-99.42%. Therefore, the energy requirement of spray drying process for MBPI could be predicted by the thermal properties of each component selected in the protein isolate.
Downloads