Numerical and Experimental Modelling of Small Hydropower Turbine
Keywords:
screw turbine, low head turbine, CFD, physical model, small hydropower stationAbstract
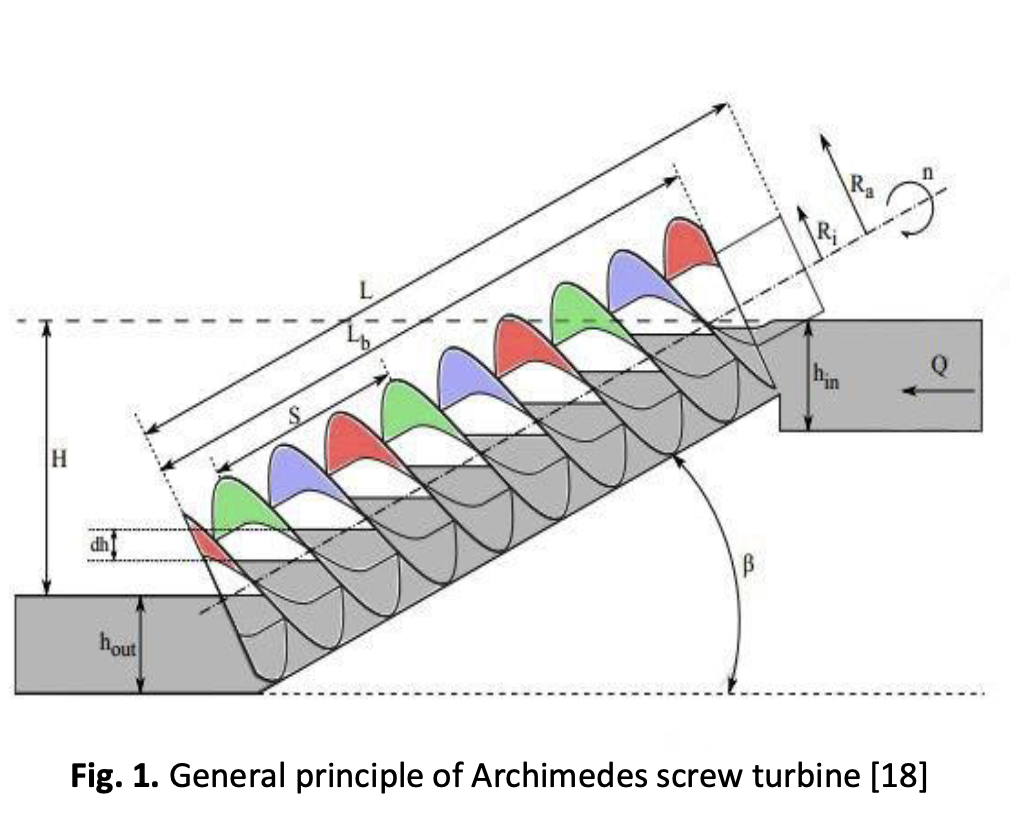
Recently, Archimedes screw turbines have been developed to operate as small hydropower stations, because of its reliability to operate with the low head (less than 5 m) and its low cost of design and operation. In the present study, the influence of the flow rate, shaft inclination angle, and the number of blades is studied using physical and numerical model to determine the performance of Archimedes screw turbine at Ramadi Barrages in Iraq. The physical model was made of stainless steel with the following parameters: (the radius ratio is 0.536, the pitch is 70 mm, the shaft angles are 30⁰ ,35⁰ ,40⁰ ,45⁰). The experimental work on the physical model is achieved with different flow rates and angles. The results showing that the highest efficiency is 81.4 % at the angle of 35⁰ and the flow rate is 1.12 l/s. The maximum energy obtained is 25.13 w at the angle of 45⁰, the flow rate is 2.065 l/s, and the efficiency was 72%. Also, the results show that the increase in the number of blades increases the torque and efficiency of the turbine.
Downloads