Vacuum Infusion Simulation for Radome Manufacturing Using Woven Flax Fibre and Glass Fibre
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.3.4956Keywords:
Permeability, Vacuum infusion, Mould design, Aircraft radomeAbstract
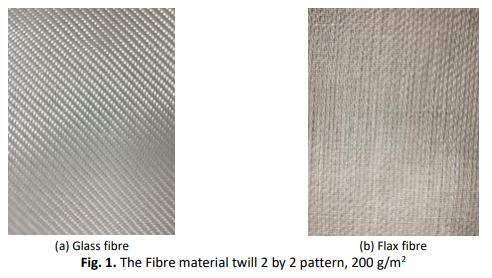
The vacuum infusion method is emerging to produce composite parts, especially thin wall structure aircraft radome. Ansys Fluent is used in the optimization phase for mould filling analysis on aircraft radome part. The permeability fibre is referring to the physical property of the fibre reinforcement to allow fluids to permeate it, thus it is correlated with the viscosity of the resin used. In this work, flax fibre, glass fibre and low viscosity epoxy resin are used to determine the permeability value of flax fibre, glass fibre and hybrid without using a flow medium. In-plane experiment on reinforcement fibre permeability is conducted and all reinforcement fibre have similar fibre architecture and weight. The development of a digital model from a top partial aircraft radome is obtained through a 3D scanner and CATIA. Ansys Fluent is used to optimize the location of the injection line and air vent for the epoxy. The Ansys Fluent analysis model is validated through the in-plane experiment filling time result for a flat model. Based on the simulation analysis, the location of the injection line is placed at the perimeter and the air vent at the centre. The filling time from the simulation for the flax fibre and hybrid fibre was estimated around 10 to 11 minutes. However, the filling time for glass fibre is approximate 2 hours which is longer than epoxy gel time. Furthermore, this method can be used in mould filing scenarios of thin wall structure within gel time of the resin.
Downloads