Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste Utilisation for Production of Low Thermal Conductivity Cement Sand Bricks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.88.3.117136Keywords:
PET plastic bottle, sand replacement, thermal conductivity, insulation, cement sand brickAbstract
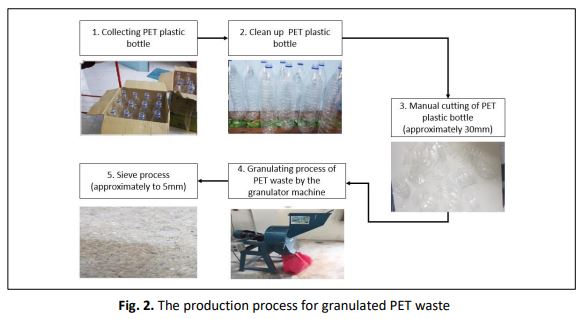
There is a tremendous increase in plastic waste that negatively impacts the environment due to various industrial activities. Furthermore, plastic waste has non-biodegradable properties that make it hard to reduce its accumulation around the globe. Hence, this study aims to investigate the possibility of incorporating Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) waste as a partial replacement material of sand to improve the thermal insulation properties of cement sand brick by looking at findings of low thermal conductivity value. The study uses a PET plastic bottle that has been cut into small flakes and grind using a granulator machine to produce PET waste granules whose size is not more than 5 mm, similar to the sand size. This waste was added to other raw materials, i.e., cement and sand. The percentages of PET waste vary from 2.5%, 5%, and 7.5% by weight. This study produced two types of samples, i.e., control brick and PET waste cement sand brick. All samples undergo laboratory works involving geotechnical gradation, physical, mechanical, and thermal conductivity testing. Based on the results obtained, the optimum proportion of PET waste replacement in cement sand bricks making is 5% by its having the lowest thermal conductivity value of 0.581 W/mK and meeting the standard requirements of 3.90 MPa > 3.45 MPa (ASTM C129-11 for compressive strength), and 2,146 kg/m3 > 2,000 kg/m3 (ASTM C129-11 for normal weight non-loadbearing brick). Thus, PET plastic bottle waste can be a potential partial sand replacement material in cement sand bricks. Its potential to enhance the thermal conductivity of existing cement sand brick reduces sand consumption, solves plastic waste problems, and promotes a better environmentally-friendly construction industry.