Analysis of Preferential Flow at the Front Mesh Cartridge of the Gas Mask Filter: Cases in Malaysia Climate Environment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.28.3.299311Keywords:
hypertension, Aneurysm, middle cerebral artery, fusiform, wall shear stressAbstract
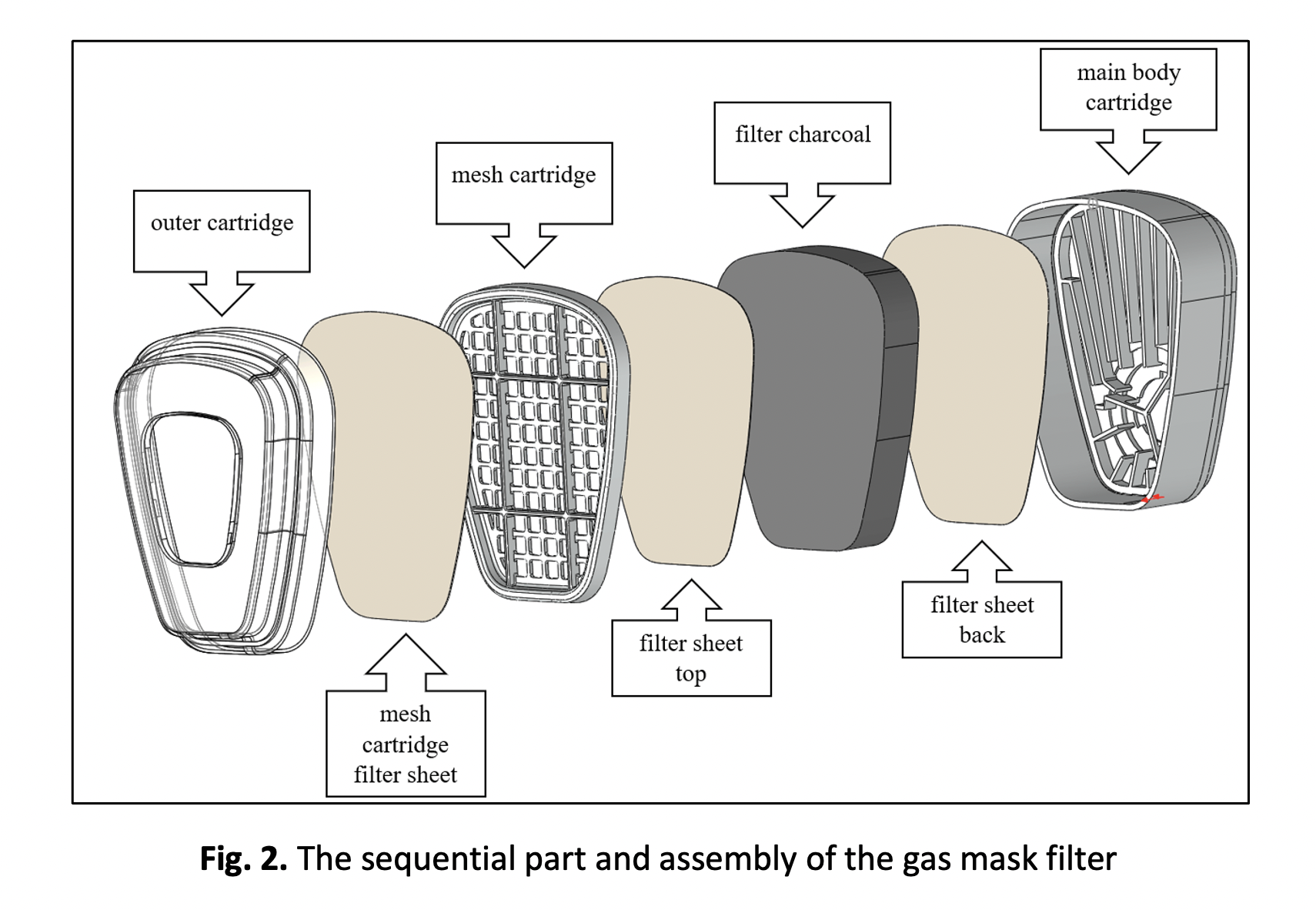
A gas mask respirator is essential for human protection from the hazardous and toxic chemical environment. The gas mask filter should be regularly checked, and the filter must be changed abruptly based on the temporal exposure to the toxic environment. Furthermore, the filter is exposed to a highly humid climate, and the high gas concentration speeds up the expiry cycle of the gas mask filter. Thus, this study aims to investigate the preferential flow absorbed into the gas mask filter and predict the potential area that presents the dead zone. In this study, a three-dimensional model of the commercial gas mask filter was modeled using the computational aided design (CAD) software. Four different humidity ratios of 50%, 60%,70%, and 80% as well as Five different filter concentrations of 20ppm, 100ppm, 200ppm, 300ppm, and 1000 ppm were simulated. The computational fluid dynamic (CFD) method was governed by continuity and Navier-stokes equation to investigate the presence of the dead zone based on several flow parameters. The result showed that the effects of the pressure, velocity, temperature, humidity, and concentration on the gas mask filter were analyzed. The pressure drop is seen in the charcoal filter region which experiences high-velocity circulation. The highest effect on the pressure drop, humidity, and concentration was seen for the case V filter. The high humidity ratio with the pressure drop in the gas mask filter also decreases the efficiency of filter concentration even though the temperature is constant. The high humidity ratio in the mask filter will retain the heat inside the gas mask filter, thus reducing the life cycle of the filter.
Downloads