Numerical Study on the Effect of Miniaturized Impeller Diameter on Mechanical Performance in a Left Ventricular Assist Device
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.28.2.2633Keywords:
Computational Fluid Dynamics, Left Ventricular Assist Device, MiniaturizedAbstract
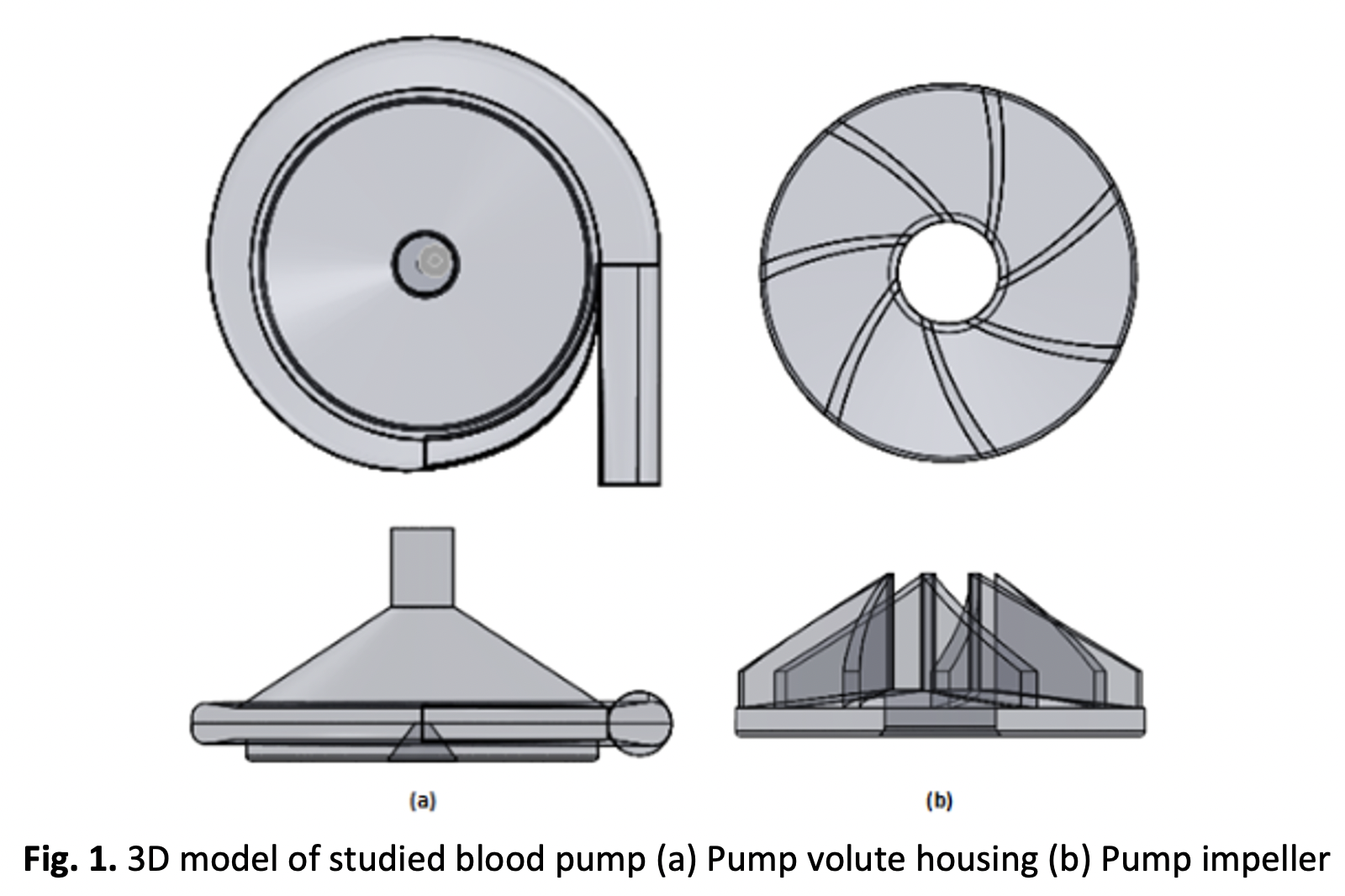
Heart failure continues to be a major global health problem causing significant health issues and deaths. Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) was developed as an alternative to heart transplant to support the patients with severe end stage heart failure. Despite the current advancement of LVAD, constant improvements are always being made in making it smaller LVADs tailored for patients with smaller physiology while still maintaining the flow ventricular pump capability to the body. This study evaluated the effect of using a smaller sized LVAD using Computation Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and compared with the initial pump size at their respective designed rotating speed. Two model variants were studied, the initial design with 44.8mm diameter impeller (2000 rpm rotating speed) and the smaller 37.0 mm diameter impeller (2500 rpm rotating speed). These designs were compared by their key criteria mechanical performances particularly the produced pressure difference along a range of flowrate and the efficiency curve. At the required flowrate of 5 L/min, the smaller sized 37.0 mm impeller was able to deliver the flowrate at a slightly higher pressure difference of 114.60 mmHg as compared to the 44.8 mm impeller at 106.01 mmHg. In overall, both model variant produced similar pressure-flowrate curve with the 37.0 mm impeller performing marginally better at higher flowrates. Efficiency was able to be maintained at 49-60 percent despite being a smaller impeller at a faster rotating speed. Miniaturizing the LVAD has been numerically demonstrated to be feasible to produce the needed flow output at the required pressure difference without affect efficiency significantly .Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2022-10-17
Issue
Section
Articles



























