Economical Aspect of Truss Design through Geometry Configuration
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.1.105114Keywords:
Truss frame, Geometry, Economical designAbstract
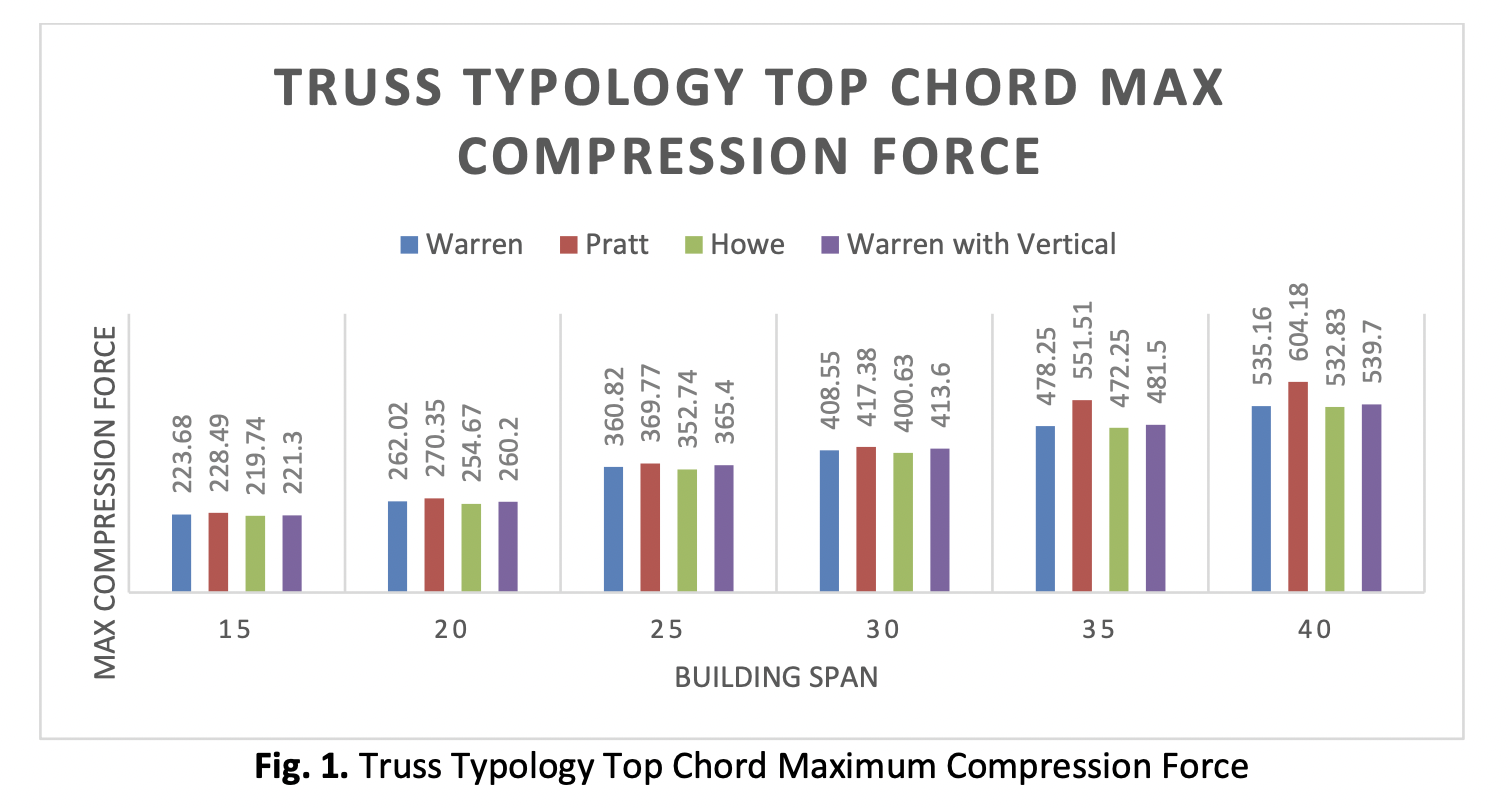
In engineering, truss structures are used extensively in bridge, tower, building, and numerous mechanical applications. Several studies have found that truss frames use the least steel weight when compared to other structural systems. The majority of truss frame design optimization research concentrated primarily on minimal weight design, and constructability, ease of fabrication, steel wastes, and the ideal geometric design parameter were not considered during the design optimization. Since the acceptable value range for factors like the span to depth ratio, truss frame typology, and diagonal angle is broad, there is no clear direction on how to determine the economical idea of truss frame geometry. To find the ideal geometry configuration for a truss frame, parametric studies were carried out, considering the truss frame span to depth ratio, truss frame typology, and diagonal angle. The study's conclusion offers a well-organized framework for choosing the best truss frame shape. According to the study's findings, there were no appreciable changes in the internal forces generated by the chords of the different truss typologies that may have resulted in substantial weight discrepancies. If constructability is a consideration, Warren trusses are a superior choice. When compared to proposals made by diverse sources, the projected truss span to depth ratio was significantly smaller. The study also showed that the member weight remains constant and does not significantly rise within a given range of the span to depth ratio.
Downloads