Structural and Morphology Changes in PrMnO3 Manganite Induced by Ba (x=0.33) Doping
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.29.3.160167Keywords:
Manganite, Structural, Morphology, X-Ray DiffractionAbstract
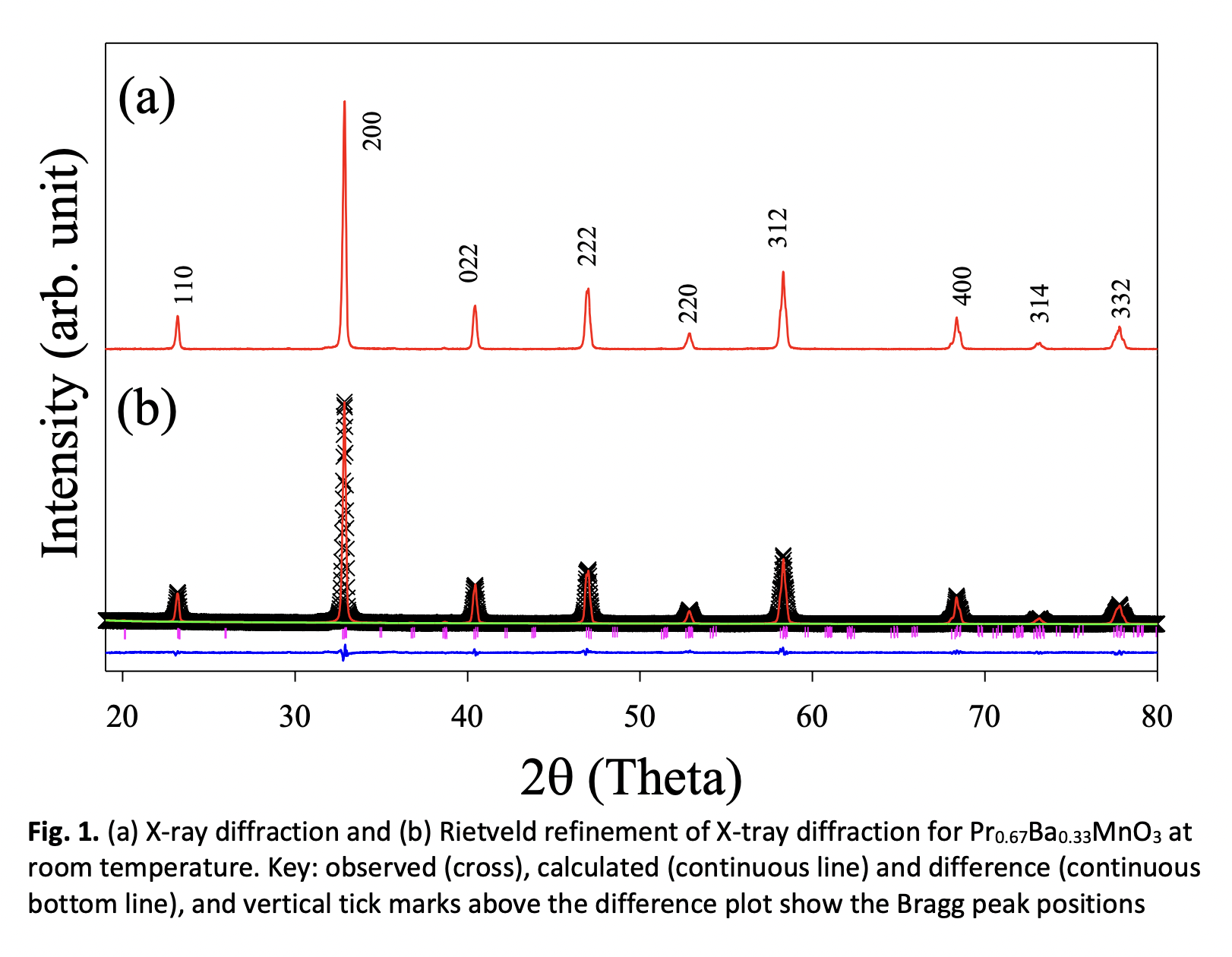
In this paper, we discuss the structural and morphology properties of the solid-state prepared Pr0.67Ba0.33MnO3 perovskite manganite X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were utilised to examine the structure, morphology, and chemical composition. The compound exhibits a single phase with an orthorhombic perovskite structure with a Pnma space group without any impurities. The refined cell parameters are a = 5.504 Å, b = 7.778 Å, and c = 5.528 Å (α = β = γ = 90° and a ≠ b ≠ c), therefore the cell volume is 236.723 Å^3. The tolerance factor is used to predict the stability of the Pr0.67Ba0.33MnO3, which is τ = 0.9241. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) reveals that the Mn-O bonds appear at 600 cm^(-1). In addition, morphology SEM revealed that the grain sizes are heterogeneous, and the grain shapes are irregular. Using EDX technique, the percentage elemental composition of Pr, Ba, Mn, and O was determined. The values of the atomic percentages for each element are almost identical to the ratios of the elements during sample preparation.
Downloads