The Effects of Different Concentrations of Nanoclay in Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) nanofibres- Polyester Bilayer on Morphological Structure, Mechanical Properties, and Filtration of Direct Red Dye
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.1.359367Keywords:
Electrospinning, polyvinyl alcohol, filtration, direct red dye, tensile strengthAbstract
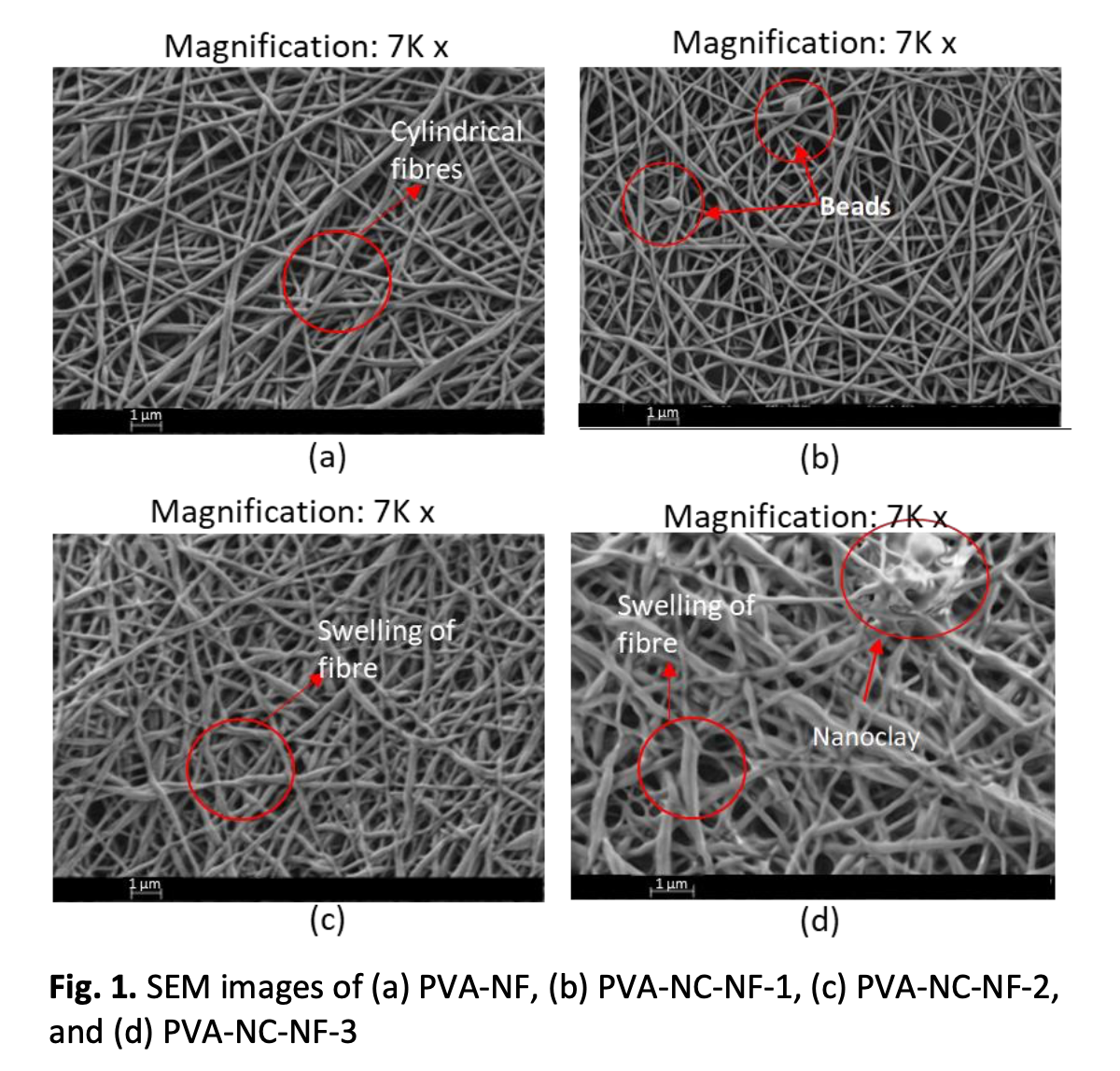
Nanofibres produced by electrospinning have high porosity, low basis weight, high surface area, and controllable pore size, which can be applied in various applications such as solar cells, supercapacitors, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, wound dressing, chemical and gas sensing and photocatalysis. However, nanofibres have poor filtration properties, particularly in textile wastewater due to the poor colour adsorption by the fibres. Hence, the study aimed to improve the filtration properties of the nanofibres by developing a bi-layer membrane of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres-polyester woven with different concentrations of nanoclay. In this study, the nanoclay was added to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) solution, which was electrospun using electrospinning to make PVA/nanoclay with polyester bi-layer. The analysis shows that the addition of nanoclay resulted in good adsorption of direct red dyes since direct dyes are often used in textile industry, indicating an improvement in the filtration properties. The tensile strength and Young’s modulus of samples decreased with an increase in the nanoclay concentration due to the fibre becoming stiffer in the bi-layer sample.
Downloads