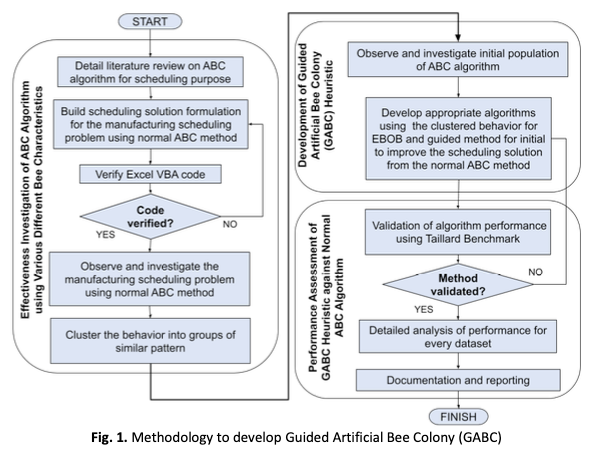
Development of Guided Artificial Bee Colony (GABC) Heuristic for Permutation Flowshop Scheduling Problem (PFSP)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.3.393406Keywords:
Guided Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm, flowshop scheduling, scheduling optimizationAbstract
The flowshop is the most often used production system in the sector, and several efforts have been made to improve its efficiency. The NEH (Nawaz, Enscore and Ham) heuristics are one of the promising techniques. The range includes using heuristics and metaheuristics. By adopting a modified version of the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algorithm, which has the disadvantage of a slow converge speed, this study aims to boost NEH. To find high-quality results with a faster convergence rate, this study developed a strategy to increase the convergence speed of ABC. Because of the significant performance in the makespan value (performance indicator), the Total Greedy was adopted in this study, and the author continued to use it throughout the remainder of the research. This study suggested creating a Guided Artificial Bee Colony (GABC) using the First Job Sequence Arrangement Method and the NEH idea. The investigation was based on Taillard benchmark datasets. According to the findings, ABC frequently gave inconsistent outcomes, but surprisingly, GABC, NEH-based ABC, and ABC consistently produced results that were each 68.75%, 63.33%, and 0.01% better than NEH. Finally, the author can state that this analysis validated ABC's slow convergence problem solutions.
Downloads