Comparison of Machine Learning Models in Forecasting Reservoir Water Level
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.3.137144Keywords:
Deep learning, early water release decision, forecasting model, machine learning, reservoir water levelAbstract
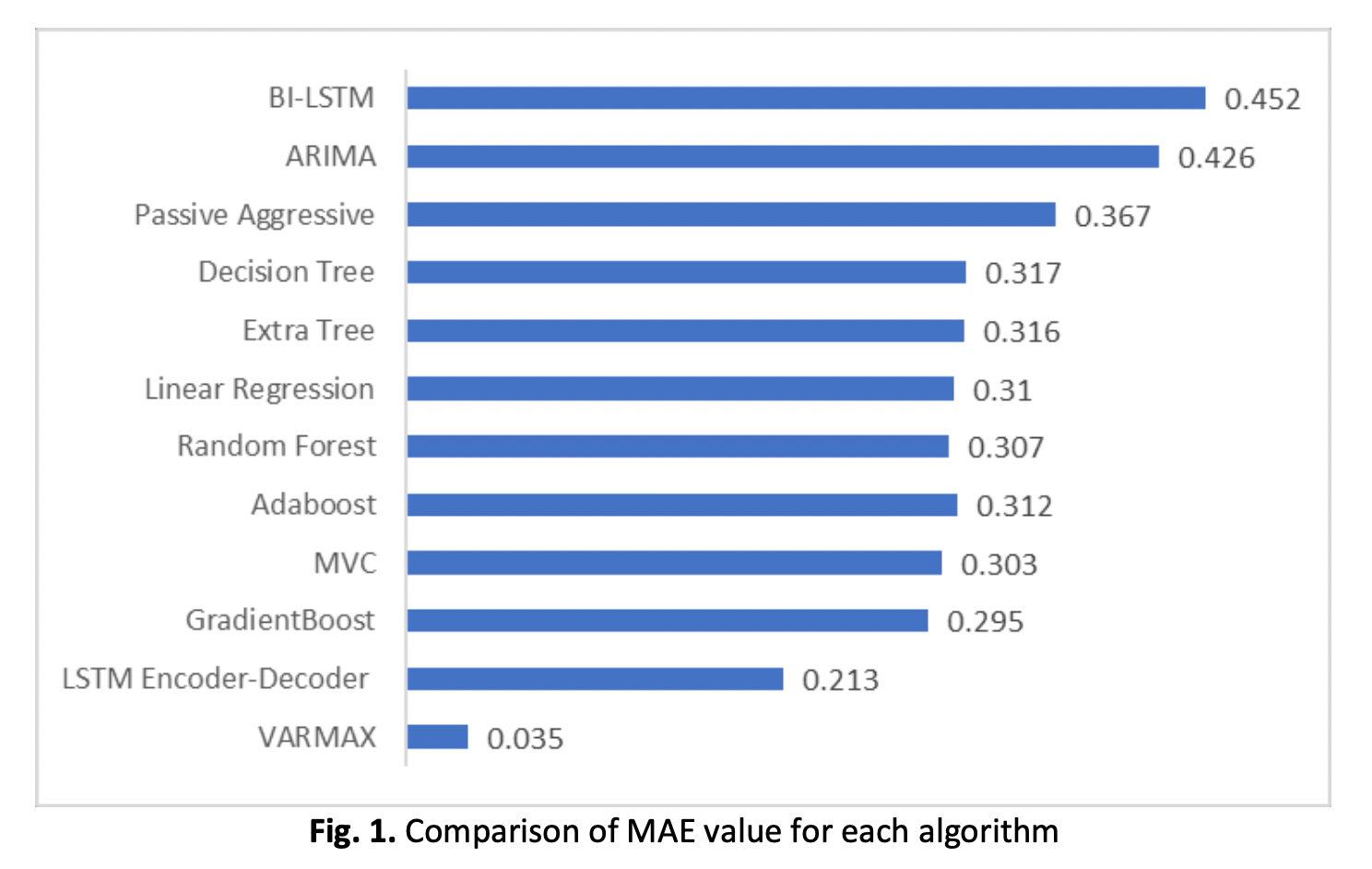
Reservoirs are important for flood mitigation and water supply storage. The reservoir water release decision, however, must be intelligently modeled due to the unknown volume of input. The model can help reservoir operators make early water release decisions during heavy rainstorms and hold water during drought seasons. One of the promising techniques has been a machine learning-based forecasting model. Therefore, in this study, several machine learning models were identified and compared in terms of performance using Mean Absolute Error (MAE), R-Square, and Root Mean Square (RMSE). The findings show that VARMAX has the highest R-squared value. This identifies the data set as a time series having a seasonal component. ARIMA, on the other hand, is unable to produce adequate results when a seasonal component is included. Both models' MAE and RMSE values accurately reflect the above-mentioned argument.