Power Efficiency Analysis based on Lightning Effect on Large-Scale Solar Photovoltaic System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.2.1930Keywords:
Lightning protection, lightning impulsive transient, induced current, power efficiency, solar PV farmAbstract
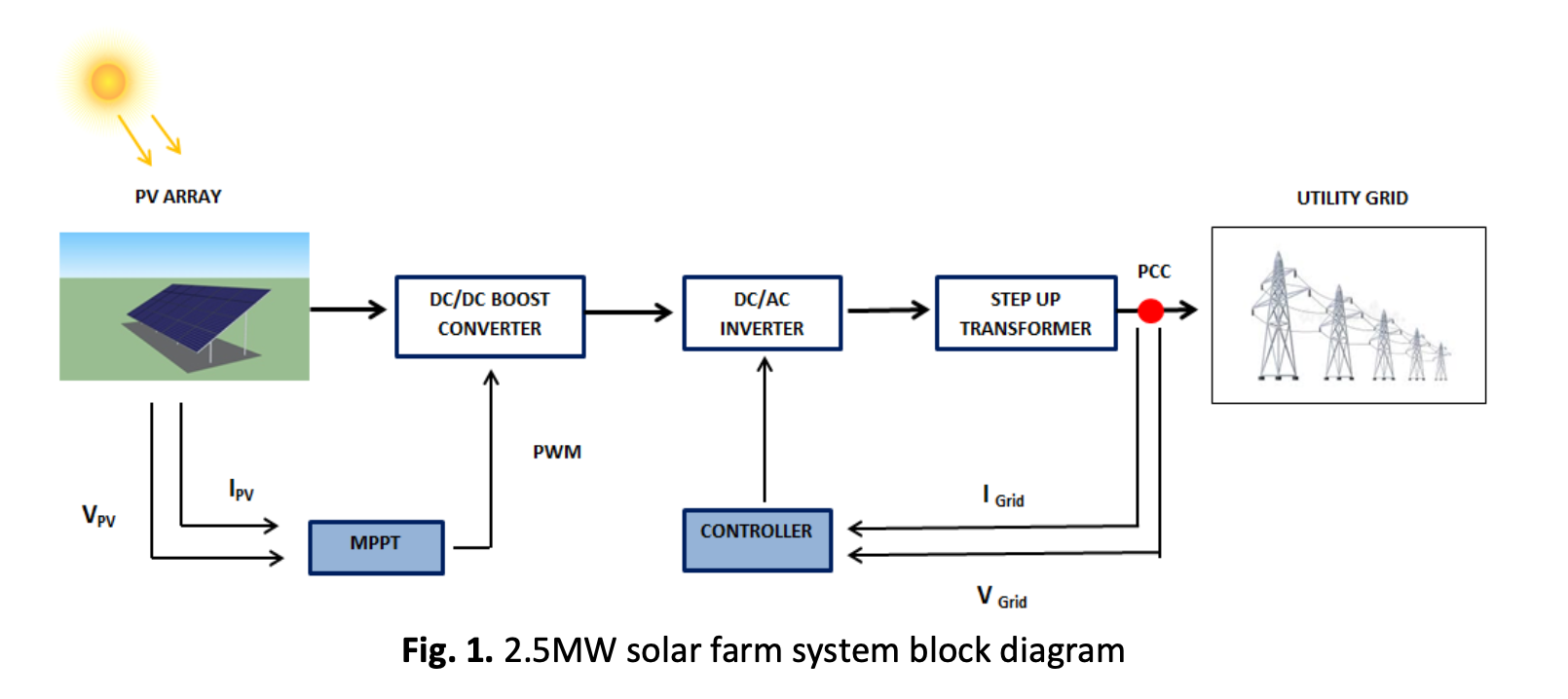
Currently, a large-scale solar photovoltaic (LSSPV) has become one of the fastest developments of electrical generation power for Malaysian Renewable Energy. However, lightning strikes are common in Malaysia due to its geographical position and tropical climate, especially in the open space of large-scale site power plants. This paper discussed the scientific basis and key assumptions that should be included in the layout of a lightning protection scheme in a large-scale solar photovoltaic installation. The framework proposal aims to ensure compliance with standards and guidelines, mitigating the risk of significantly induced currents in the LSSPV power plant. A 2.5 MW solar PV farm system was modelled using MATLAB software for assessing a solar PV farm’s electrical performance under various lightning current waveforms and lightning magnitude currents. These lightning strikes will impact photovoltaic modules, thus deteriorating the system’s ratio generation. The effects of lightning current on LSSPV were accessed based on simulation work in MATLAB Simulink. The induced current protection scheme covered rating selection and collecting data on lightning that may hit the modules or arrays. This data was then analysed according to the standard guidelines to ascertain the most effective protection measures for the 50MW PV farm within the LSSPV system. Minimising the maintenance and replacement cost of equipment is possible. The performance of a 2.5MW solar PV power plant with a grid connection was evaluated. A maximum and minimum power output of 2.47MW and 522.50kW, respectively, were observed. However, when the lightning impulsive current is included through the system, the power output decrease to 407.33kW due to the high magnitude induced.Downloads
Downloads
Published
2023-07-19
How to Cite
Nurul ‘Aini Mohamad Zakaria, Mohd Najib Mohd Hussain, Intan Rahayu Ibrahim, Nor Salwa Damanhuri, & Nor Fadzilah Ahmad. (2023). Power Efficiency Analysis based on Lightning Effect on Large-Scale Solar Photovoltaic System. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 31(2), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.2.1930
Issue
Section
Articles




























