Case Study of the Effect of Tilt Angle on Output Power and Efficiency of Photovoltaic Using Two Solar Irradiation Measurement Methods
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.1.2536Keywords:
tilt angle, output power, efficiency, photovoltaic, solar irradiationAbstract
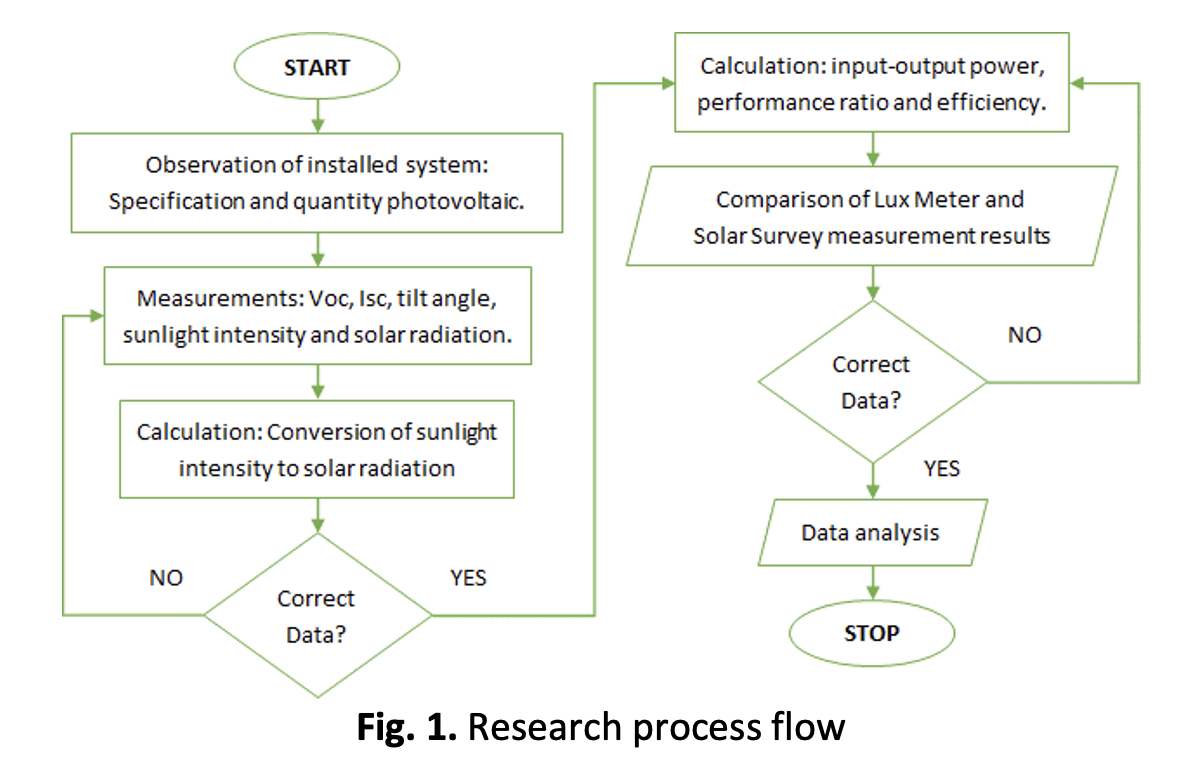
Geographically, Indonesia has huge renewable solar energy, which is potentially utilized as a source of electrical energy. The latest photovoltaic technology can be applied to effectively harvest electrical energy. Correspondingly, the small power plant of 50 kWp is currently installed at Pamulang University. Meanwhile, solar radiation and tilt angle have a significant impact on photovoltaic efficiency. So, a case study is needed on the effect of solar radiation and tilt angle on the output voltage open circuit and current short circuit to determine the influence on photovoltaic efficiency. This case study compares two measurement methods of solar radiation, measurement of photovoltaic voltage and current under existing tilt angle conditions. Only a 5.0 % difference in solar radiation using the Lux Meter 721 W/m2 and Solar Survey 684 W/m2 is a non-significant difference, so both measuring devices are feasible to use. The difference in efficiency is only 5.2% with measurements using a Lux Meter of 19.3% and a Solar Survey of 20.4%, this value is better than the ideal efficiency value of 20.6% in conditions of the existing photovoltaic tilt angles are 2°, 4° and 6°. This means that the angle of inclination does not have a significant effect on efficiency, but this efficiency is strongly influenced by the value of solar radiation.Downloads
Downloads
Published
2024-01-24
How to Cite
Ojak Abdul Rozak, Mohd Zamri Ibrahim, Muhamad Zalani Daud, Syaiful Bakhri, & Tri Eka Oktavian. (2024). Case Study of the Effect of Tilt Angle on Output Power and Efficiency of Photovoltaic Using Two Solar Irradiation Measurement Methods. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 38(1), 25–36. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.1.2536
Issue
Section
Articles




























