Examining the Effectiveness of Thinking Maps Usage by Analysing Students' Achievement in Mathematics Subject
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.1.197209Keywords:
Experimental, Mathematics, student achievement, Thinking MapsAbstract
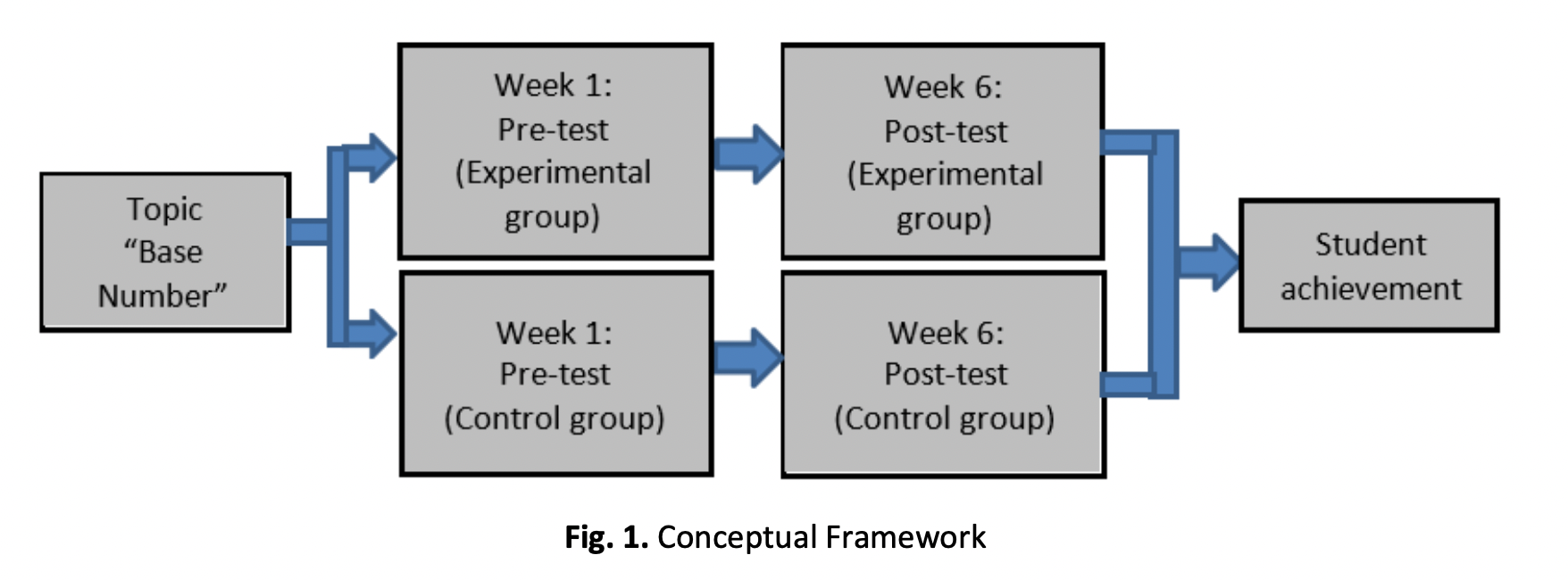
Teachers play a critical role in ensuring their pupils succeed in their studies. Educators must select acceptable teaching methods to ensure an effective learning experience. By applying the t-test statistical analysis, this research aimed to evaluate the efficiency of the thinking maps approach with traditional ways in increasing student achievement for a number base topic. This study involved 120 Form 4 pupils from 4 schools in Pahang. This research implemented a quantitative approach (quasi-experimental method). The research featured an experimental group (n = 60) and a control group (n = 60). As research tools, a set of pre-test and post-test inquiries were used. The application of thinking maps improved student achievement in mathematics subjects. There was a substantial difference in mean scores between the control and experimental groups, where the mean score of the experimental group seemed to be higher than that of the control group. Additionally, mean scores before and after the teaching and learning sessions showed a positive increase in both categories. Nevertheless, compared to the control group, the experimental group that utilised thinking maps showed a higher ascent in the mean score. The findings of this study can assist teachers to develop a thinking map as one of the teaching approaches for improving pupils' knowledge of a topic and, therefore, indirectly improving pupil academic achievement.
Downloads