Handover Network Selection for Vehicle in LTE-A Communication Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.1.373382Keywords:
Handover, relative direction index, proximity index, residence time indexAbstract
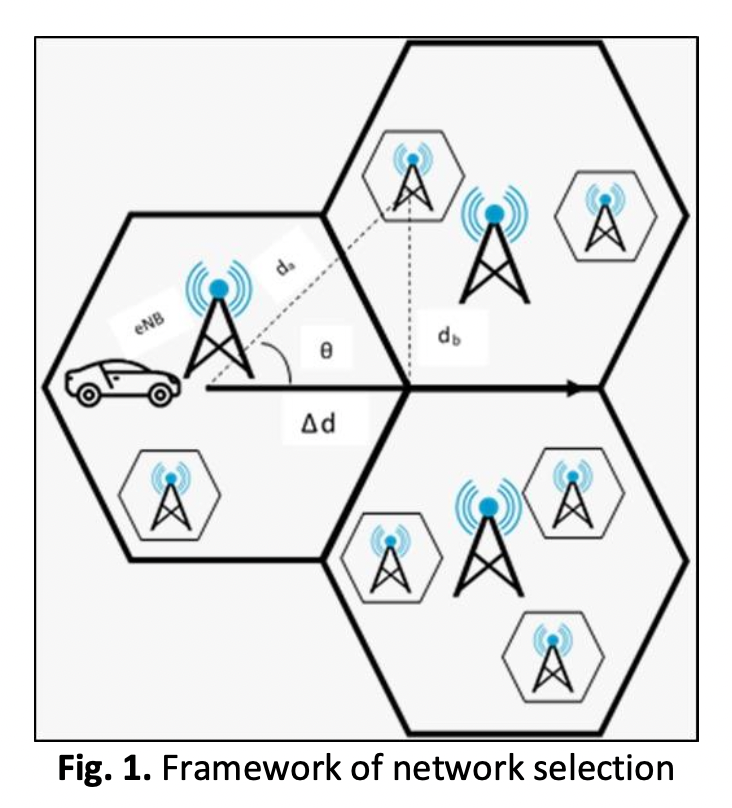
One of the challenges to achieving smooth communications in heterogeneous networks is to find the right balance between various handover parameters for network selection. The Receive Signal Strength (RSS) from a network's Point of Attachment (PoA) is the primary factor used in traditional approaches to network selection. Therefore, network selection is vital for a successful handover in the vehicle communications network. However, vehicles moving through such diverse networks faced difficulties like frequent unwanted handovers, selecting the wrong candidate networks for handovers, and taking too long to finish the drawn-out handover procedure, which results in failed handovers. All of these factors will impair the efficiency of the handover process, which will affect the smooth operation of the vehicles. Hence, the main idea of this research is to improve the handover network performance selection performance. The proposed work is for vehicles to self-evaluate a candidate list of Access Points (AP) that are located in the vehicle movement direction and select the best underlying candidate network. In this project, the network selection framework of the vehicle communications network with the distance between the target candidate and the trajectory of the vehicle movement was developed as well as the vehicle mobility information. The important parameters which are the relative direction index, proximity index and residence time index are chosen to identify the best candidate network. Once the target of the base station has been identified, then the optimum value of the distance is calculated using the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) technique to initiate the handover process. The performance of the proposed handover network selection is simulated and evaluated using MATLAB software. The results show that the proposed handover network selection method improved the successful handover rate as compared to the conventional method.