Sustainable Industrial Revolution Competency Framework for 5G Technology Applications using TRIZ
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.3.336344Keywords:
The sustainable industrial revolution, Framework, Competency, 5G technology, TRIZAbstract
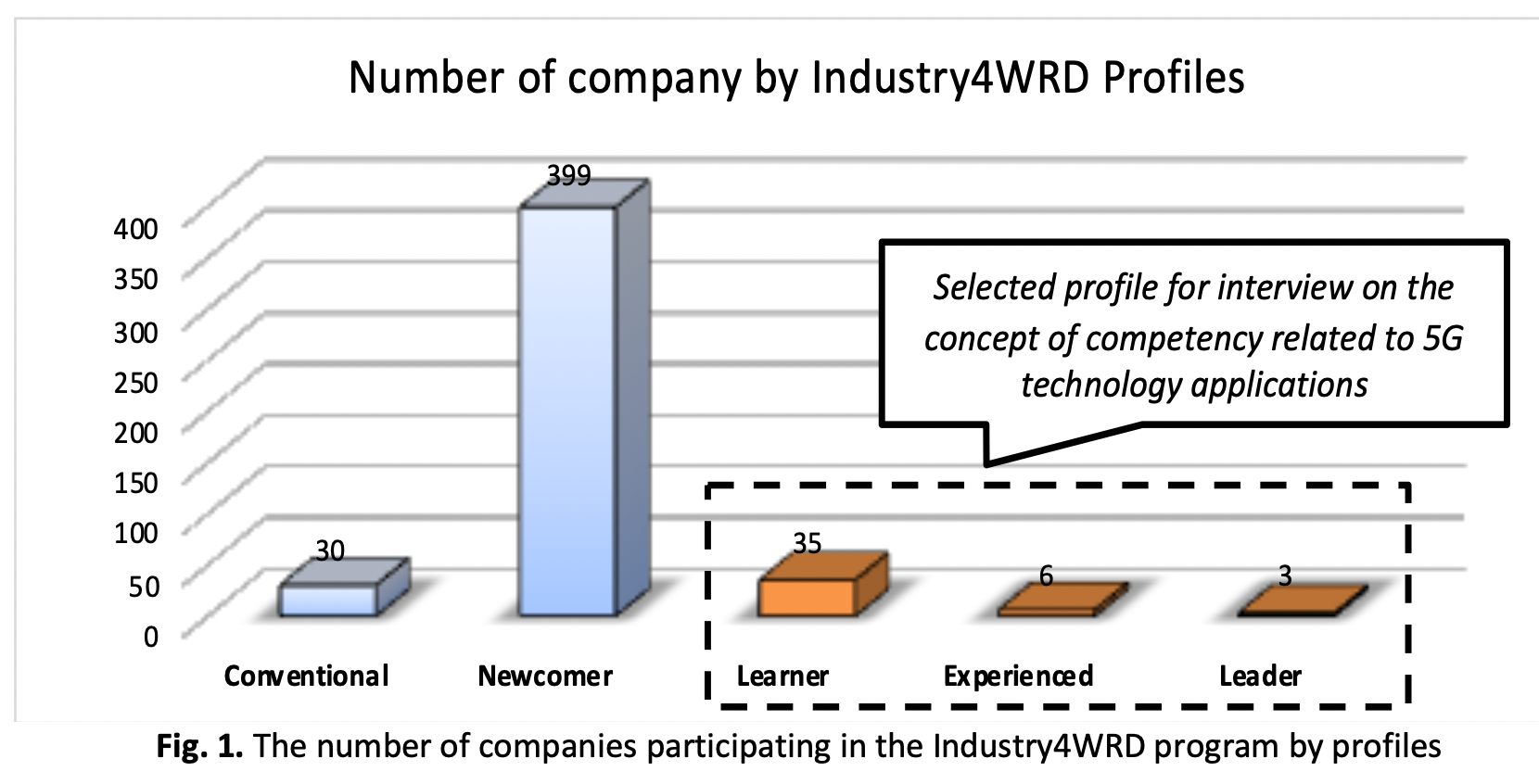
The Malaysian industrial revolution strategy, also known as Industry4WRD, has been the driving force behind the transformation of the industrial sectors by accepting and implementing modern technology. The initial phase of the Industry4WRD initiative focuses on the readiness assessment of industrial businesses to determine their level of adoption of Industry 4.0. However, the second phase challenges firms to advance and increase their readiness index. According to data collected from 473 firms, the 'People' shift element has the most significant obstacle for companies to overcome, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs). In the 'people' dimensions of Industry4WRD, the research emphasised the importance of competency in developing human capital for 5G technology applications. The benchmarking technique revealed five skill levels, the competency unit and work activities associated with 5G telecommunications and system networks. The theory of creative problem solving (TRIZ) was applied to a system-based idea to develop a conceptual competence framework. Twenty-five firms were selected and contributed to this research by designing and verifying a conceptual competence framework for 5G technology implementation. With a 0.81 concordance coefficient, the study's objective has been accomplished by obtaining a high level of unanimity across 25 organisations in three rounds of the Delphi poll. As a guideline, the conceptual competency framework may be utilised to create other technology competencies, such as automation and artificial intelligence workforce. It would benefit the country to conduct more research on the specifics of competence units depending on the needs of industrial sectors.
Downloads