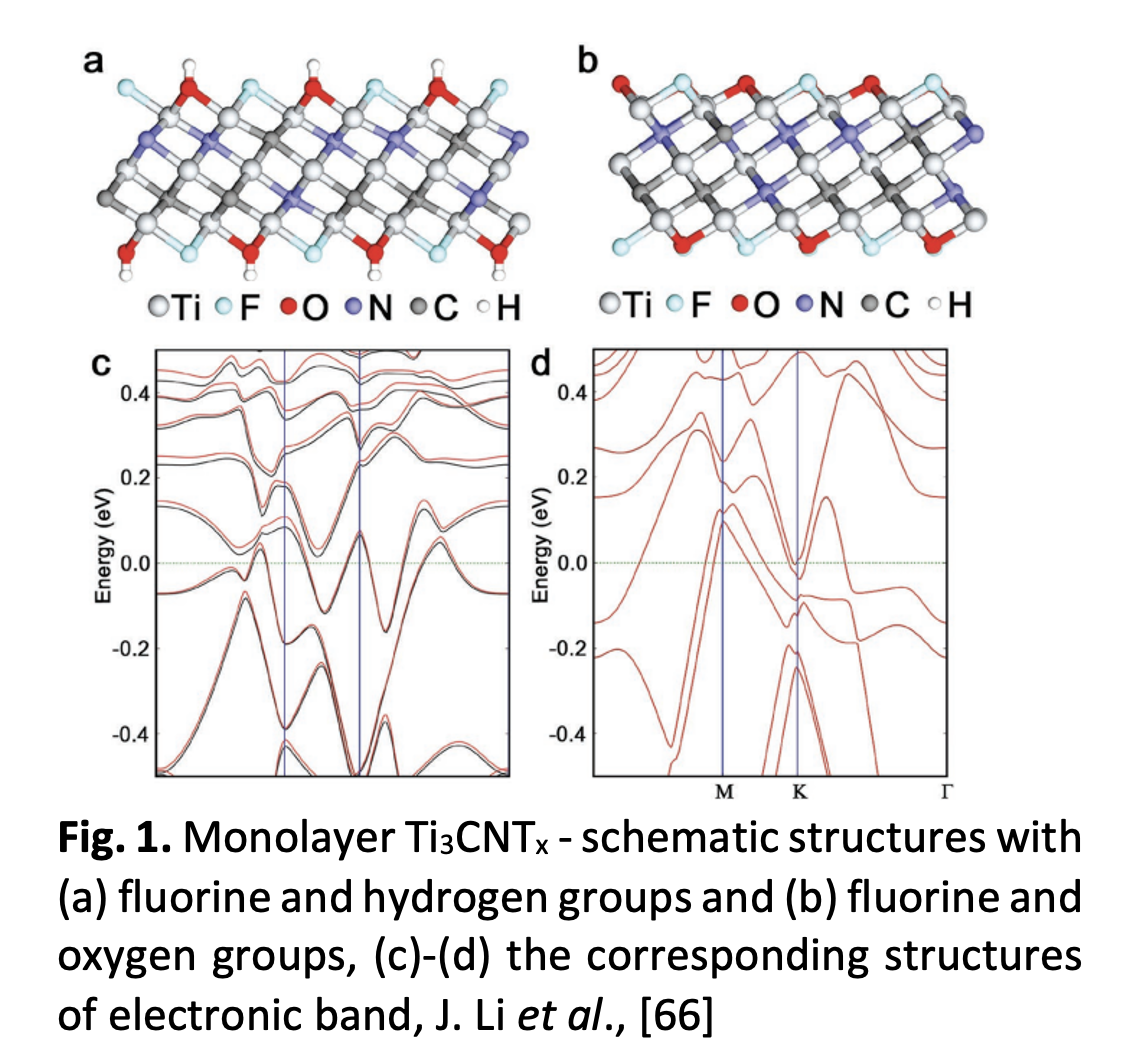
Synthesisation, Fabrication, and Incorporation Techniques of MAX Phase and MXene Saturable Absorber in Passively Q-switched and Mode-locked All-fibre Laser Cavities: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.119141Keywords:
MAX Phase, MXene, saturable absorber, all-fibre laser, passively mode-lock, passively Q-switchAbstract
MAX phases and MXene have been introduced in passively pulsed-laser generation for their viability as substitutes to unadventurous saturable absorbers such as saturable absorber mirror, multi-wall and single-wall carbon nanotube, graphene, and transition metal dichalcogenides, contributing to both Q-switching and mode-locking tactics. Fundamental saturable-absorber features such as nonlinear saturable absorption, astonishing depth of modulation, flexibly tuneable bandgap, and high electron density around the Fermi level, establish MAX phases and MXene as formidable contenders with decent performance in the saturable absorber regime. Recent research works contributing to MAX Phases and MXene—particularly in nonlinear ultrafast optics—have shown an exponential increase, since MAX Phases and MXene are of the prime regime of 2D nanomaterials that offer vast combination options by the formation of metal nitride, metal carbide, or carbonitride clusters with a 2D layered structure, with special emphasis on fabrication and incorporation of saturable absorbers into laser cavities. This review critically summarises the advancement on the synthesis, fabrication, and incorporation of the MAX phases and MXene saturable absorbers, as well as the incorporation methodologies and techniques into all-fibre laser cavities configured either in linear or ring configuration, summing up the identified issues and challenges and discussing future perspectives of this novel material.
Downloads