Discovering and Recognizing of Imbalance Human Activity in Healthcare Monitoring using Data Resampling Technique and Decision Tree Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.2.340350Keywords:
Human activity recognition, imbalance data, SMOTE-Tomek, healthcare, MARDA Dataset, Decision tree, synthetic minority over-sampling samplingAbstract
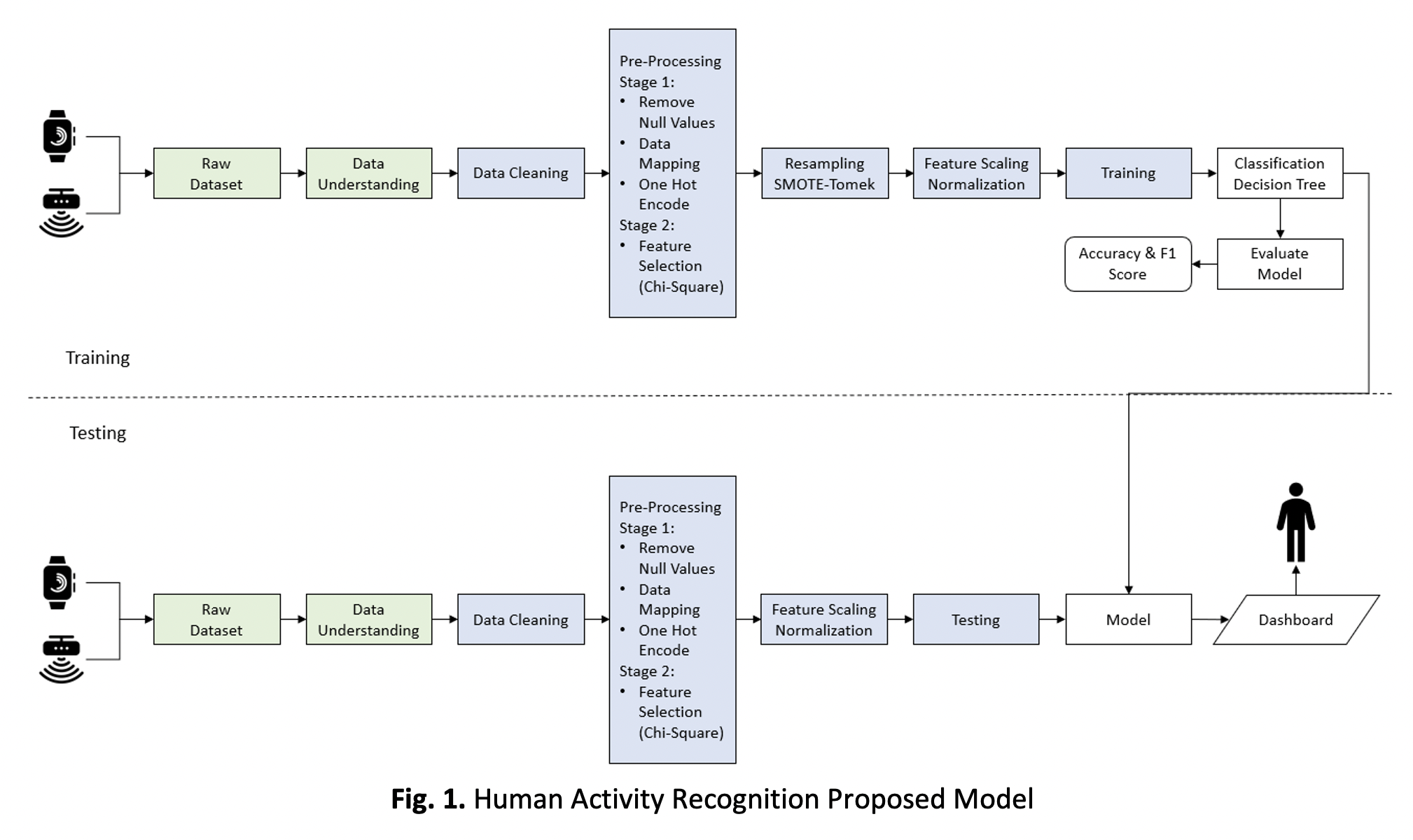
Human activity recognition model is vital and has been use in healthcare monitoring system. Bespoke multi-modal sensors were used such as accelerometer, gyroscope, GPS, temperature, pressure mat etc. Hence, the activities involved may varied resulted on class imbalance issue therefore, the model accuracy also degraded and may not provide the desired results in all aspects. Resampling method addressed as Synthetically Minority Oversampling Technique and Tomek Link (Smote Tomek) is proposed to balance the target classes. Moreover, many classification algorithms such as Logistic Regression, SVM and Decision Tree were selected for the experiments on two datasets namely MARBLE that was publicly available and MARDA dataset. The classification accuracy of 98.36% for the MARBLE dataset and 97.45% for the MARDA dataset. While executing the classification model for training and testing data, the time has also been calculated for time efficiency. The Decision Tree model has the fastest execution time compared with other models. The execution training time for MARBLE and MARDA were: 6.51ms, testing: 12.90ms and, training: 41.30ms, testing: 1.30ms, respectively. Subsequently, the decision tree model can be deployed in a healthcare system dashboard for effective monitoring and efficient decision making.Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
Downloads
Published
2023-11-08
Issue
Section
Articles



























