Analysis of Early Stroke Diagnosis Based on Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging using Machine Learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.3.241255Keywords:
Paralysis, blood flow blockage, neuroradiologists, magnetic resonance imaging, collateralAbstract
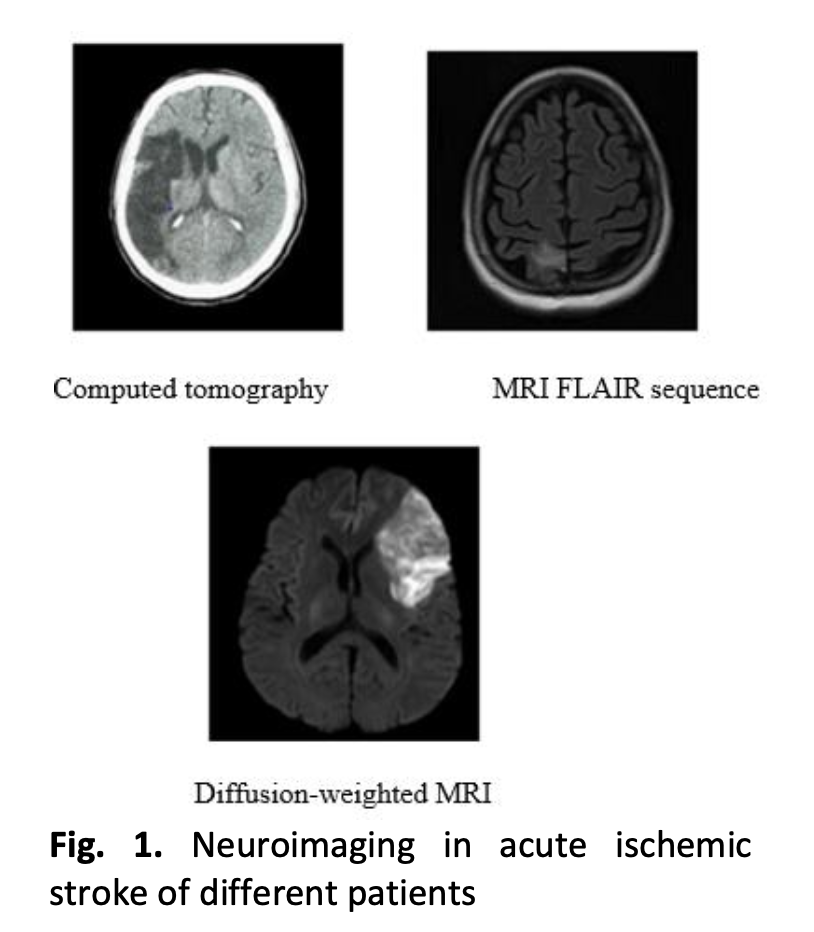
Stroke causes paralysis resulting from a hemorrhage in the brain or blockage of blood flow to the brain. It is third leading cause of death in Malaysia, with at least 32 deaths per day, and poses a major challenge to Malaysia's health services. A recent study showed that he could save a patient's life if he received treatment within six hours of a stroke. Unfortunately, Malaysia is facing a shortage of neuroradiologists, hampering efforts to treat its growing number of stroke patients. In this research, used Magnetic Resonance Imaging which is better compare to CT scan and CBCT because MRI will produce more detailed images of soft tissues, ligaments and organs. So that, advanced imaging using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has gained more attention than conventional angiography in the diagnosis of acute stroke due to its high spatial resolution and fast scan times. Traditionally, diagnosis was made manually by neuroradiologists during a highly subjective and time-consuming task. Detecting collaterals from MRI images is a challenging task due to the presence of noise and artifacts, small size, and heterogeneous structure of vessels. By the way, this paper is mainly about the early diagnosis of stroke based on brain magnetic resonance imaging using machine learning. Based on the results, can see that the Fuzzy c-means (FCM) and Watershed Transformation (WT) segmentation of brain infarcts which are original image, output of guided filter, gradient magnitude image, output of watershed transform and final detected infarct with morphological operation.
Downloads