A Comprehensive Performance Comparison of Thresholding and the K-Means Clustering Algorithm in White Blood Cells Segmentation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.55.2.203213Keywords:
White blood cells, image segmentation, thresholding, K-means clusteringAbstract
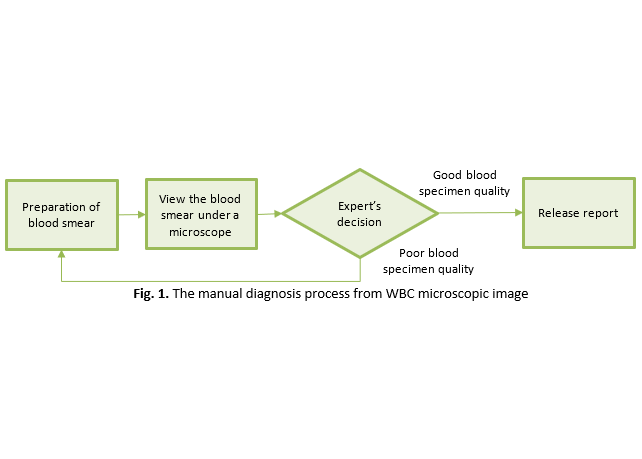
In the medical field, the segmentation of white blood cells is an important process in machine learning techniques. The conventional process requires an expert, a hematopathologist, to manually analyse blood smear samples from patients. The sample is pre-processed on a slide using a staining procedure that provides the components of platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. White blood cell images obtained by a microscope are important in guiding haematology imaging to diagnose blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma. However, there are some challenges while conducting manual segmentation of white blood cells, which requires expert labour to observe each blood sample individually to diagnose the patients. This process is also very iterative, time-consuming, and relatively expensive. Besides that, this procedure has medical and scientific drawbacks, including inaccurate output due to interobserver disagreement and inadequate sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value. Thus, new methodologies were proposed throughout the years to aid the white blood cell segmentation process. The objective of this study is to review thresholding and K-means clustering methods, which are two widely used segmentation approaches, to segment the microscopic image of white blood cells. The effectiveness of these approaches was then evaluated. The proposed methodology was tested on five types of white blood cells: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes, to compare their performances. The result shows that the K-means clustering technique's performance is more accurate than the thresholding, where the dice similarity is 93.88% and 93.23%, respectively. Contrarily, the thresholding technique runs much quicker than the K-means clustering algorithm, requiring 0.3238 seconds as compared to 6.4292 seconds.
Downloads