Problematic Internet Use and Mental Health Correlates among Children: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.34.1.257278Keywords:
Problematic Internet Use, Mental Health, ChildrenAbstract
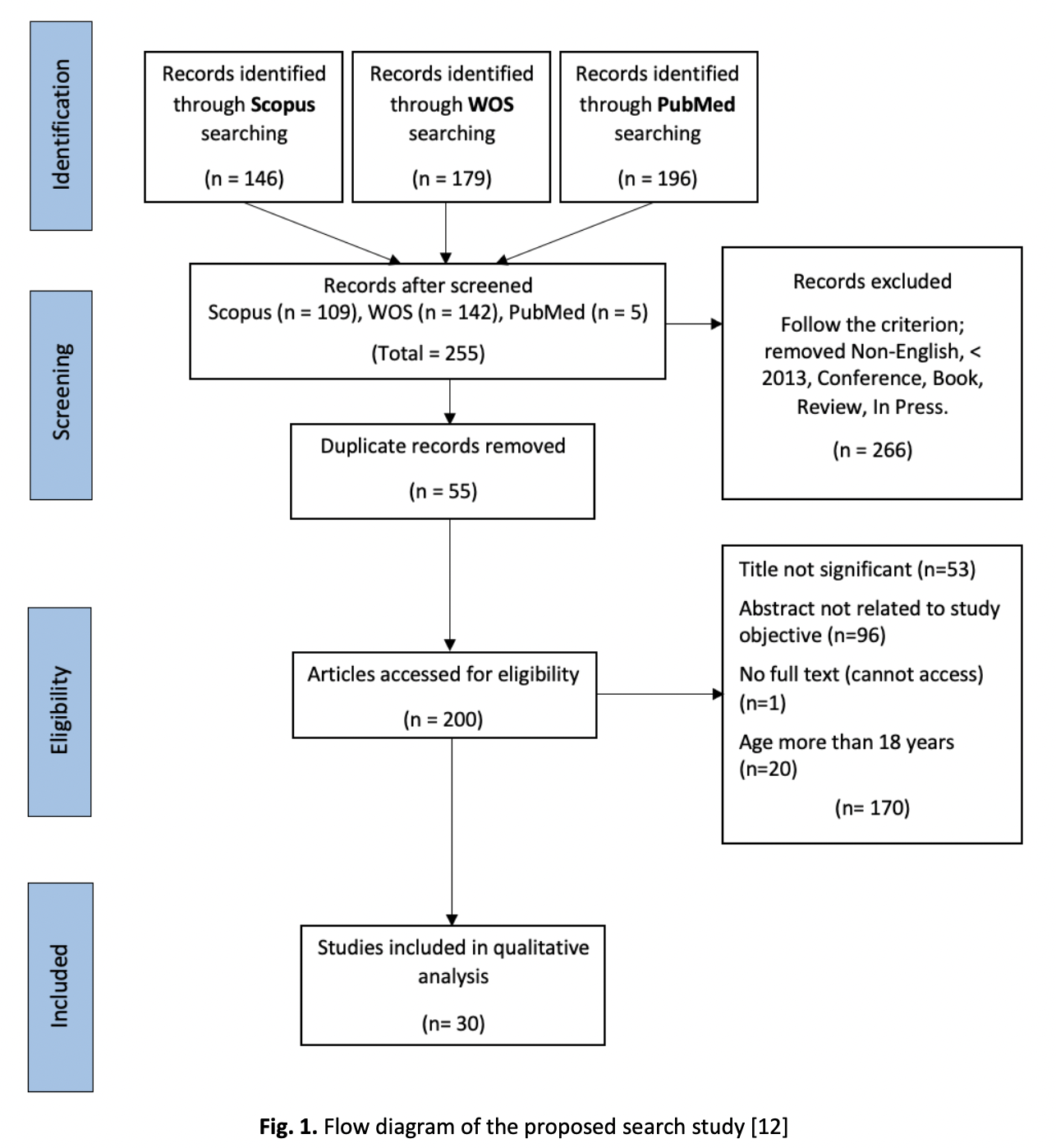
Problematic Internet use (PIU) among children is a growing concern due to its potential negative impact on mental health and overall well-being. This systematic literature review aimed to identify the association between problematic Internet use (PIU) and mental health challenges among children in order to propose appropriate interventions. A comprehensive search of three electronic databases, Scopus, Web of Science (WOS) and PubMed, yielded 30 relevant articles published between 2013 and 2022. The findings reveal a strong association between PIU and various psychiatric disorders and environmental factors. However, due to the cross-sectional nature of most studies, causal relationships between PIU and its correlations could not be determined. Two studies examining the temporal relationship between PIU and mental health challenges indicated bidirectional associations, emphasising the importance of addressing both PIU and associated mental health issues in intervention and prevention strategies. By incorporating parental involvement, school-based interventions, psychological therapies, public health policy interventions, and multidisciplinary stakeholders, we can effectively promote responsible Internet use, mitigate risk factors, and foster a supportive environment for children. In conclusion, this systematic review underscores the significant association between PIU and mental health problems among children. The findings emphasise the importance of adopting comprehensive approaches considering individual and environmental factors to address PIU effectively.
Downloads