Energy Efficient MAC for M2M Communication Using Dynamic TDMA in IoT Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.327345Keywords:
QoS, M2M communication, Grouping, MAC protocol, Markov Chain, DTDMA, HHO, CSMA/CAAbstract
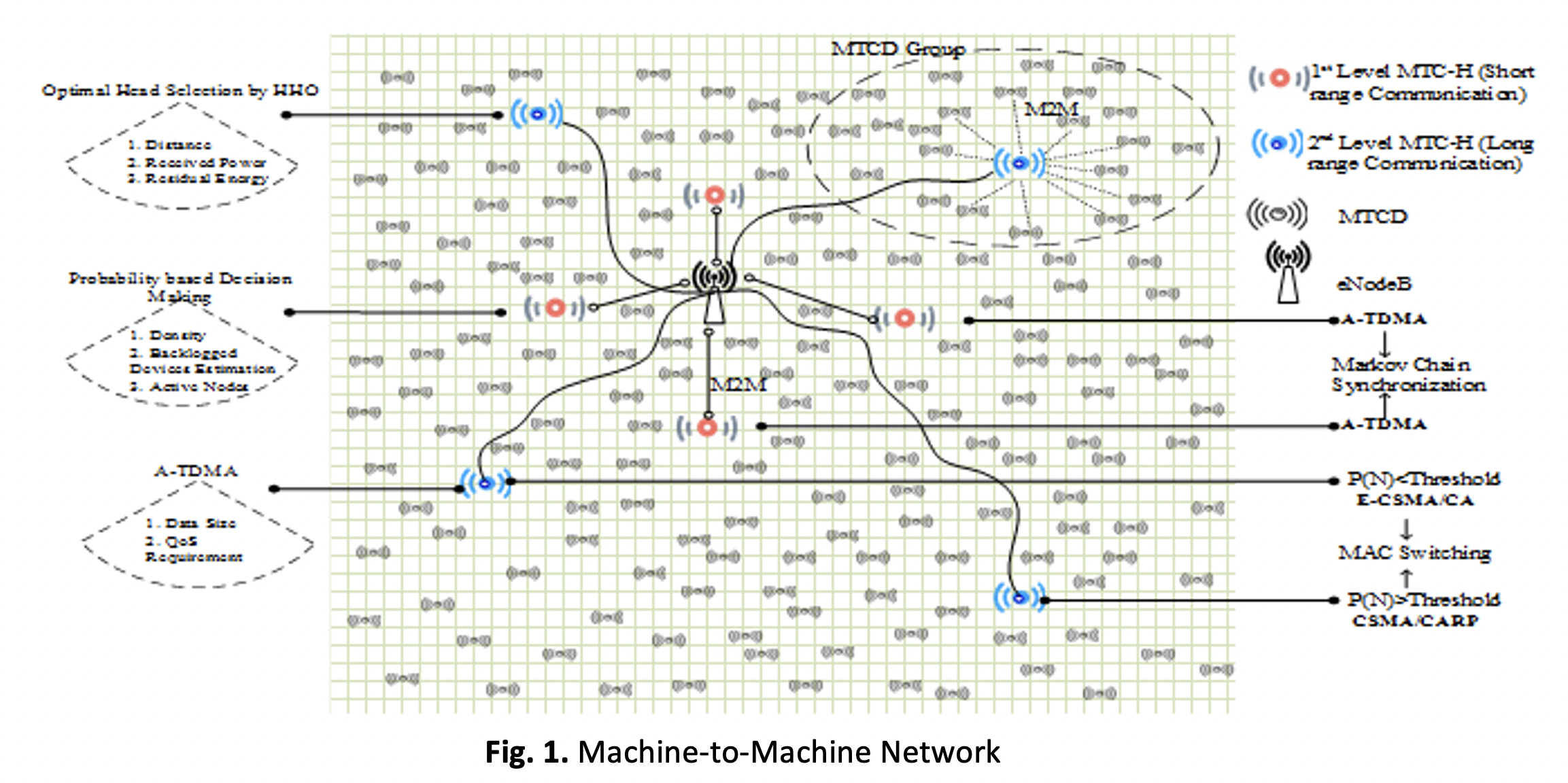
In the Internet of Things (IoT) context, the relevance of M2M communication increased, creating the need for practical solutions. MTCDs, or Machine Type Communication Devices, frequently encounter issues such as collisions and delays while transmitting data, ensuring network scalability and maintaining the quality of service (QoS) for all devices participating in the communication. To address these challenges, this paper presents the protocol for switching MAC that optimizes energy usage with Dynamic Time Division Multiple Access (EMAC-DTDMA). TheEMAC-DTDMA protocol involves grouping, dynamic MAC switching, and timeslot allocation. The Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) algorithm is applied to choose the cluster head of the machine type communication devices (MTCH) while the CSMA/CA and CSMA/CARP protocols with different backoff times are used to minimize collisions based on device density, backlog, and active nodes. The timeslots are allocated based on data size and QoS requirements using Dynamic TDMA. The Markov chain model is employed to overcome synchronization issues with traditional TDMA. The EMAC-DTDMA's performance is evaluated through simulation using a network simulator tool, considering access delay, energy usage, collision probability, and throughput.
Downloads