Fuzzy Enhanced Black Widow Spider with Secure Encryption Random Permutation Pseudo Algorithm for Energy Efficient Cluster Communication in WSN
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.3.421437Keywords:
Cluster, Energy Consumption, Internet of Things (IoT), Network lifetime, Sensor NodeAbstract
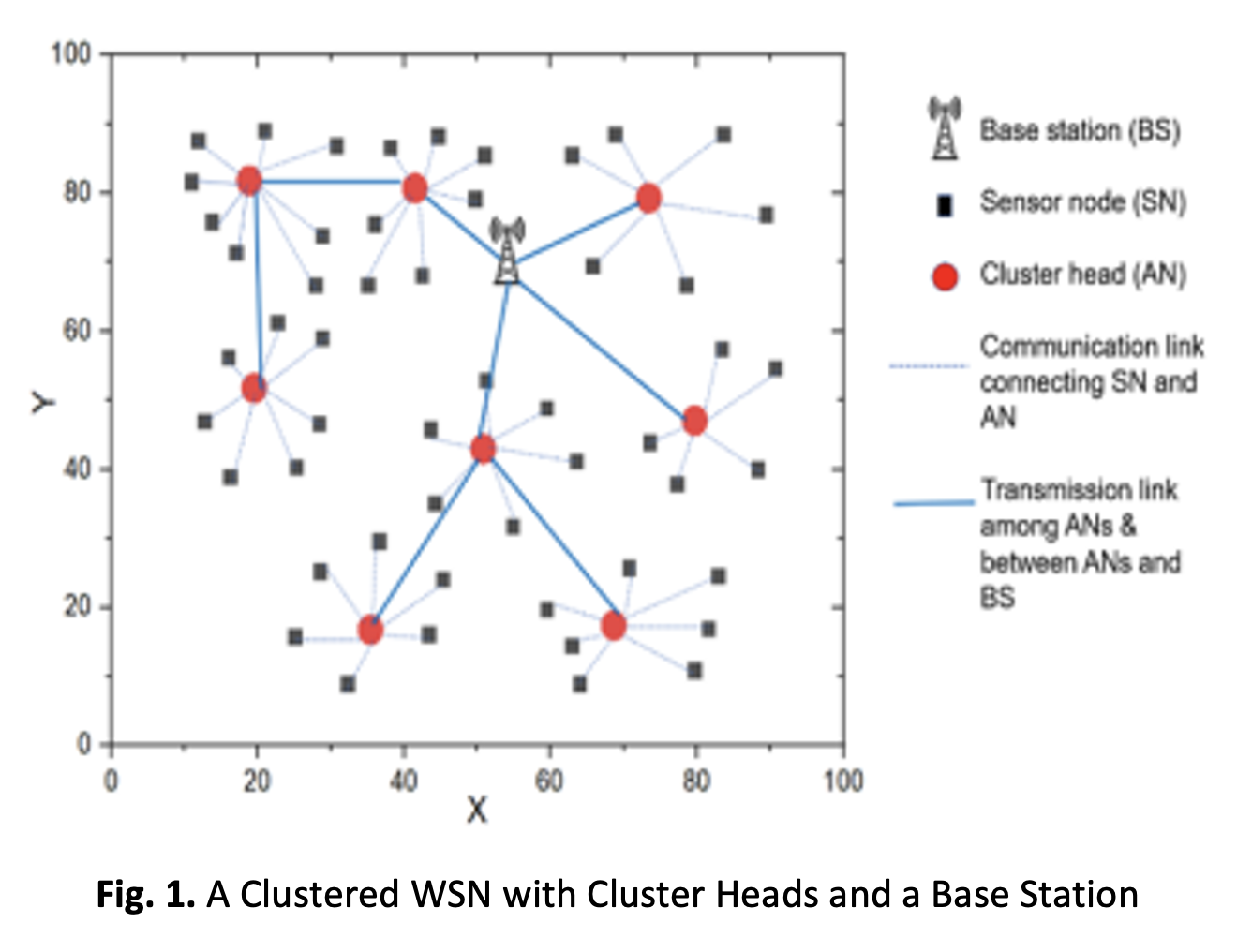
Devices connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) are increasingly being used. Modern mobile apps may be incorporated onto low-cost, low-power devices with the help of these extensions. This integration is made possible by the utilization of low-cost, low-power sensor nodes. All sensor nodes transmit data either directly or via a multi-hop path to other receivers or nodes. In order to enable effective inter-cluster communication through ideal cluster head selection, we build a fuzzy-enhanced black widow spider based on the Secure Encrypted Random Permutation Pseudo Algorithm (FEBWS-SERPPA) in this study. By taking energy, latency, and distance characteristics into account, the suggested FEBWS-SERPPA algorithm enhances the black widow spider optimization method by choosing the optimal cluster head in the cluster. To ensure its effectiveness, the suggested FEBWS-SERPPA algorithm's performance is compared to the state-of-the-art. The suggested FEBWS-SERPPA algorithm delivers enhanced performance speed with very low energy consumption and extended network lifetime when compared to existing cutting-edge methods.