A Brief Review on Ancillary Services from Advanced Metering Infrastructure (ASAMI) for Distributed Renewable Energy Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.41.2.4361Keywords:
Advanced metering infrastructure, Ancillary service, Distribution networkAbstract
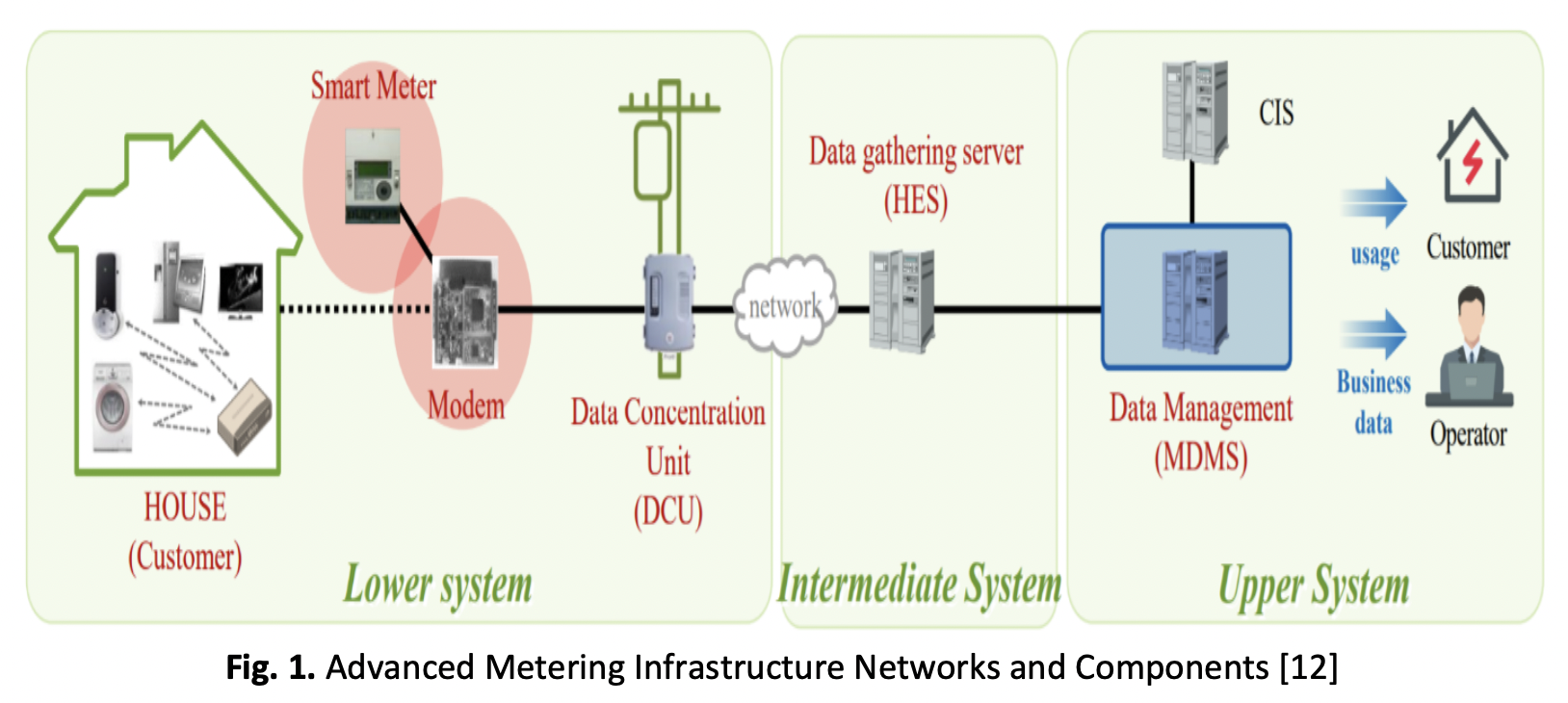
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) is an integrated system of smart meters, communications networks, and data management systems that enable the secure, effective, and dependable distribution of power while also delivering enhanced capabilities to energy consumers. The system also can measure power usage, connect, and disconnect service, detect tampering, identify and isolate outages, and monitor voltage automatically and remotely, which were previously unavailable or required user intervention. This article focuses on AMI and effectively integrating renewable energy sources (RES). However, the study also recommends smart metering for renewables such as solar photovoltaic (PV), hydropower, anaerobic digestion (ad) metering, and renewable energy storage, in which AIM thoroughly supervises the energy utilized by users' appliances. With the prediction of new ancillary services connected with contestability, related regulation, the sufficiency of consumer protection, and safety issues, the magnitude of renewable energy sources in the AMI is an almost unprecedented problem for consumers. The present energy management problems include reducing the power supply-demand gap and boosting power supply dependability. Implementing AMI with distributed renewable energy resources might be a viable strategy for lowering power consumption, improving power supply management, and maximizing management resource use.
Downloads