Toward Adaptive and Scalable Topology in Distributed SDN Controller
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.30.1.115131Keywords:
Distributed SDN controller, OpenDayligh, Controller performance, ScalabilityAbstract
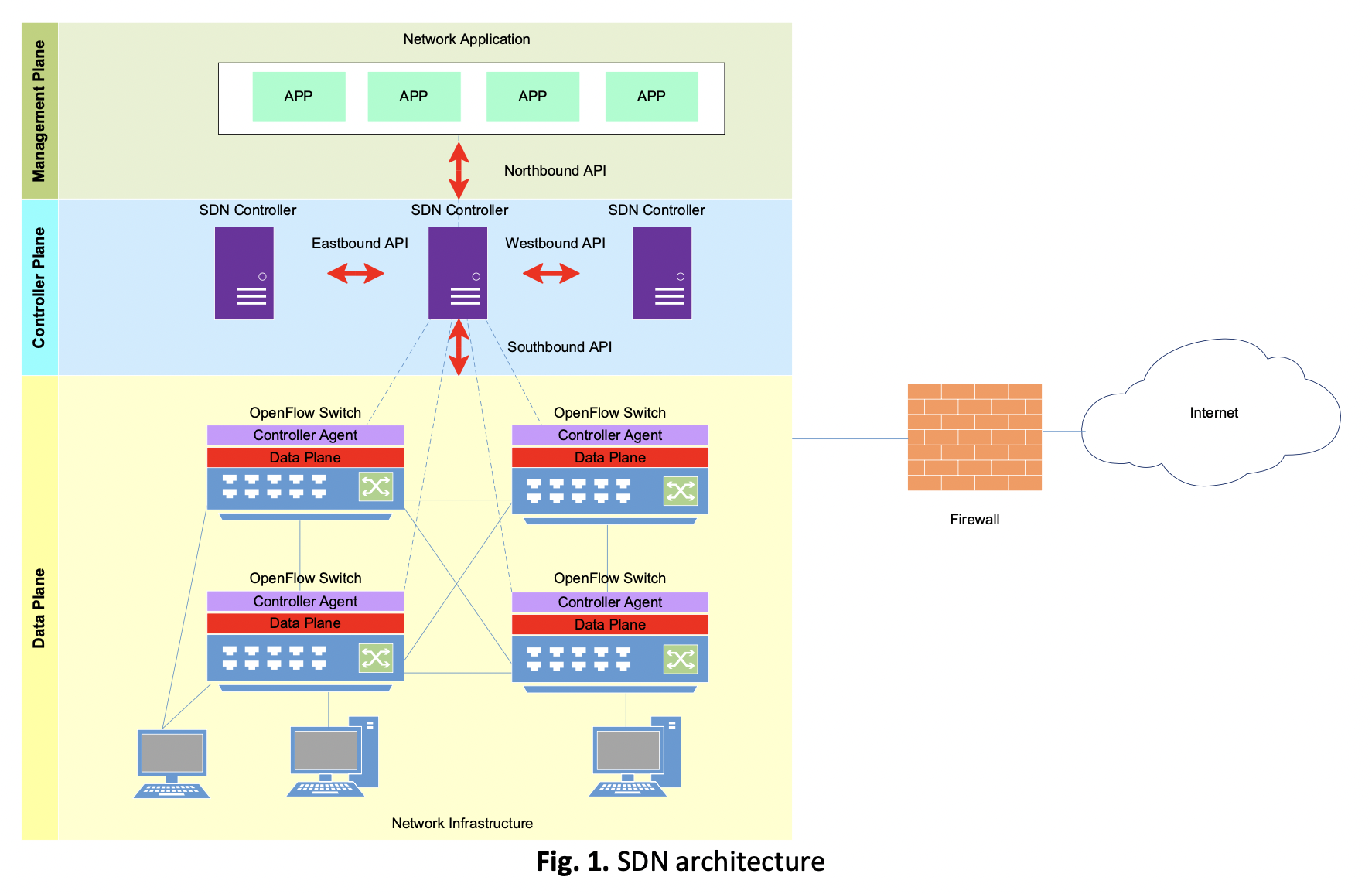
The increasing need for automated networking platforms like the Internet of Things, as well as network services like cloud computing, big data applications, wireless networks, mobile Internet, and virtualization, has driven existing networks to their limitations. Software-defined network (SDN) is a new modern programmable network architectural technology that allows network administrators to control the entire network consistently and logically centralized in software-based controllers and network devices become just simple packet forwarding devices. The controller that is the network's brain, is mostly based on the OpenFlow protocol and has distinct characteristics that vary depending on the programming language. Its function is to control network traffic and increase network resource efficiency. Therefore, selecting the right controllers and monitoring their performance to increase resource usage and enhance network performance metrics is required. For network performance metrics analysis, the study proposes an implementation of SDN architecture utilizing an open-source OpenDaylight (ODL) distributed SDN controller. The proposed work evaluates the deployment of distributed SDN controller performance on three distinct customized network topologies based on SDN architecture for node-to-node performance metrics such as delay, throughput, packet loss, and bandwidth use. The experiments are conducted using the Mininet emulation tool. Wireshark is used to collect and analyse packets in real-time. The results obtained from the comparison of networks are presented to provide useful guidelines for SDN research and deployment initiatives.
Downloads