Enhancing Heat Transfer in Compact Automotive Engines using Hybrid Nano Coolants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.314326Keywords:
Nano coolant, automobile radiator, compact enginesAbstract
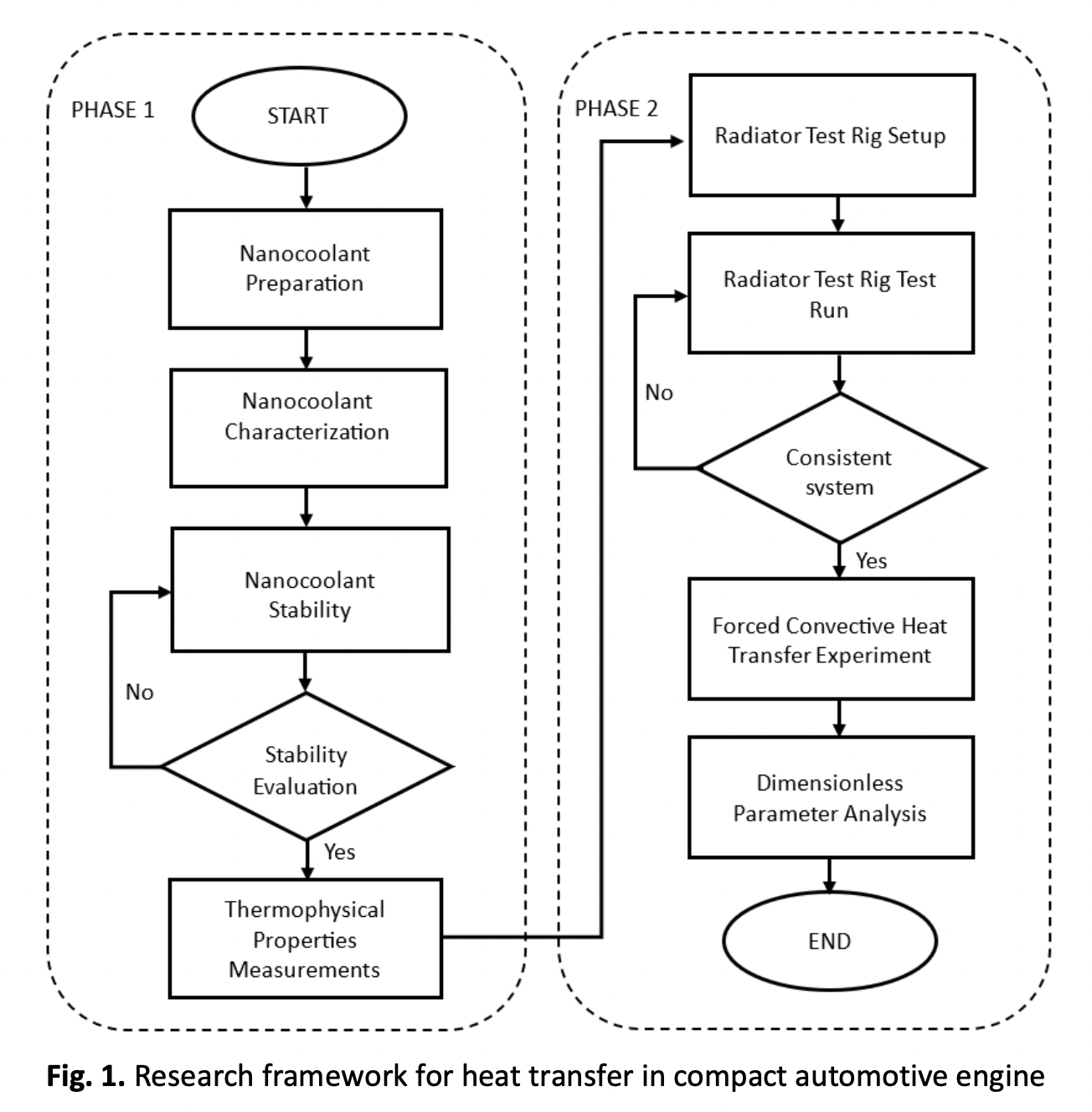
This research aimed to compare the performance of a reduced-scale automotive radiator using single nano coolant (CNC and CuO) and its hybrid nano coolant (CNC and CuO nanoparticles) to enhance heat transmission. Three ratios of 70:30, 80:20, and 90:10 of hybrid nano coolants was tested. UV Vis stability characterization of the nanofluids showed that all samples were highly stable for up to 30 days. A modest concentration (0.01 vol per cent) of the hybrid nano coolant was shown to efficiently increase the heat transfer rate of a reduced-size automobile radiator, demonstrating that the heat transfer behaviour of the nano coolant was reliant on the particle volume percentage. The results show the potential use of hybrid nano coolants in increasing heat transfer efficiency, decreasing cooling system size by up to 71 percent, and thus lowering fuel consumption; these benefits have significant implications for developing more efficient cooling systems in various industrial applications. The experimental findings showed that 80:20 exhibited a significant amount of improvement in thermal properties. The consistency of the low volume concentration of hybrid nano coolants throughout the experiment is further evidence of their promise as a practical substitute for conventional cooling media in the compact size of an automotive engine cooling system.
Downloads