Adsorption of Sodium Ion (Na+) onto Synthesized Zeolite-A from Malaysian Kaolin by Hydrothermal Method: Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.31.1.5367Keywords:
Adsorption, adsorption isotherm, kaolin, kinetic, zeoliteAbstract
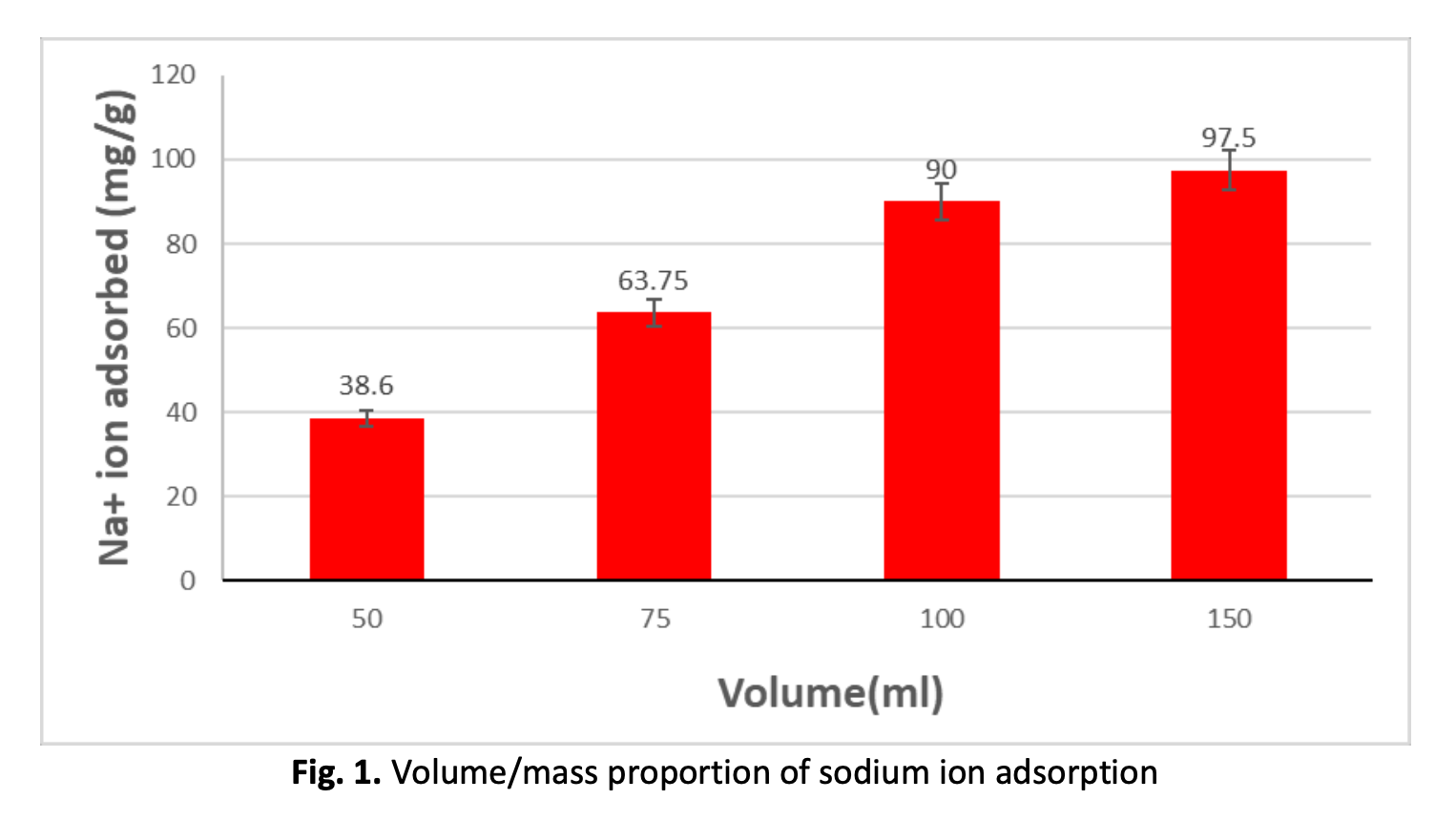
Batch adsorption of sodium ion (Na+) using Malaysian kaolin-based materials, zeolite A was studied and observed. The experiments were done at different parameters such as varying initial concentrations of sodium ions in seawater solution (70 to 280 mg L–1), pH range of 6 to 8 and various adsorbent dosages (0.1 to 0.4g). The Langmuir and Freundlich's isotherms were used to analyse the data, and the results were compared. This study discovered that the Langmuir isotherm matched the experimental data very well, with the maximum monolayer adsorption capacities derived from the Langmuir equation being 769.3 mg g–1. Using pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second order, and intraparticle diffusion models, the kinetics of the reaction were further investigated and understood. The Intra Particle Diffusion Kinetic Equation was the most accurate description of the adsorption kinetics of sodium ions onto zeolite synthesis.