The Effectiveness of Collaborative Learning in Improving Higher Level Thinking Skills and Reflective Skills
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.42.1.191198Keywords:
Higher order thinking skills (HOTs), Cognitive level, Online collaborative learning (CL), Reflective thinking (RT)Abstract
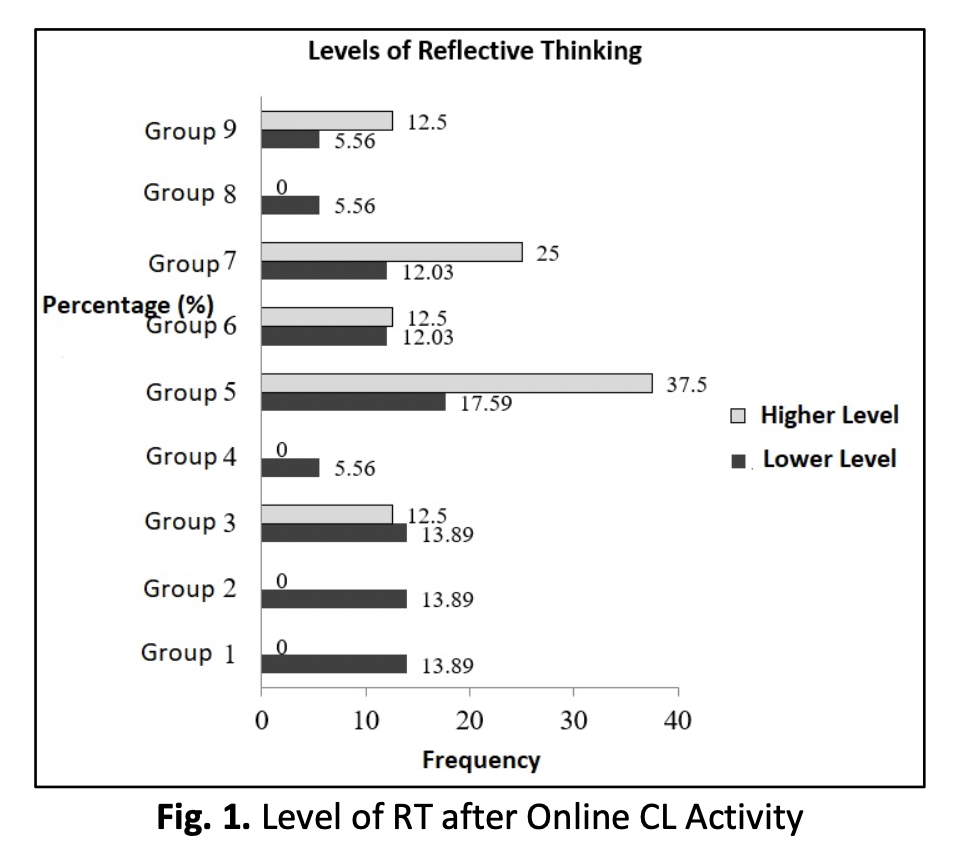
Collaborative learning (CL) is a 21st century learning approach that can improve thinking skills among students. CL strategies can improve motivation, understanding, communication and social engagement. This study attempts to evaluate the extent to which CL improves Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) and reflective thinking (RT) abilities. This study involved 34 students in the final year of the bachelor’s degree at the Faculty of Education, UTM who took the subject SPM4342 (Multimedia Based Multimedia Development). This study uses a qualitative methodology based on discussion forums and online portfolios for rubric content analysis. Analysis of the findings of the study shows that CL improves HOTs and RT abilities. Five groups out of 9 groups increased the level of thinking skills from higher to lower. When the 4 groups are in an environment of lower-level thinking skills and after being tested on the 4 groups, they are found to be inactive in the online-based CL While reflective skills increase from lower-level skills (Stimulated Reflection = 3.33% decrease and Descriptive Reflection I = 8.6% decrease) to higher-level skills (Descriptive Reflection II = 16.5% increase and Dialogic Reflection = 13.3% increase). In short, CL strategies can improve understanding and directly improve students' cognitive abilities.
Downloads