A Bibliometric Mapping Analysis of Publications on the Utilization of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Language Learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.1.156176Keywords:
Artificial intelligence technology, bibliometric analysis, language learning, mapping, publicationsAbstract
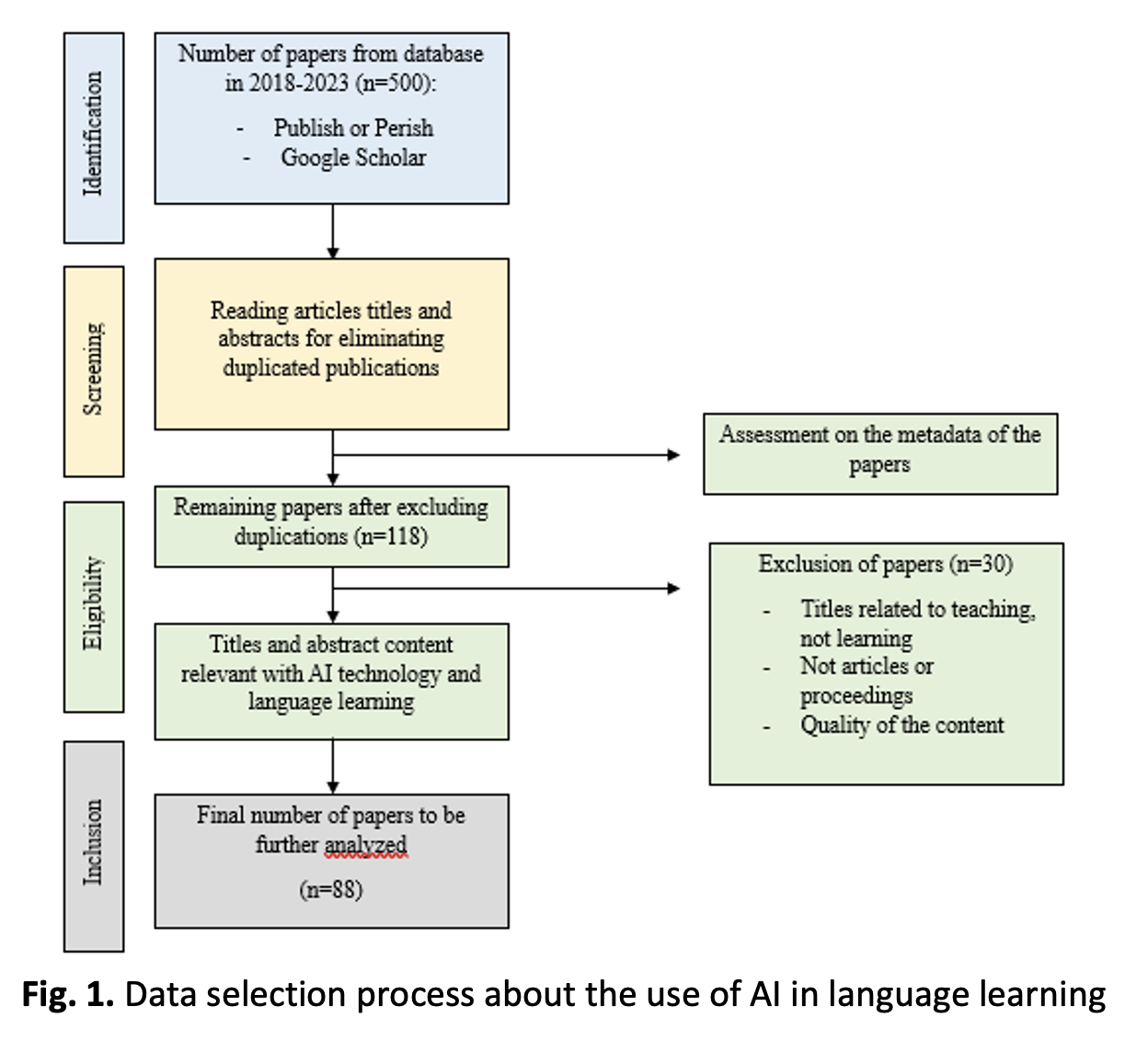
A plethora of publications have shed light, particularly on the affordances of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered technology to maximize the language learning preparation, process, and outcomes. In search of the current portrait of empirical evidence in this context, this paper reports on a bibliometric mapping analysis of publications on the utilization of AI technology in language learning in the last five years (2018-2023). Relevant studies associated with the theme were collected from several journals sorted out using predetermined criteria. Eighty-eight titles and abstracts were further reviewed to generate a mapping of relevant keywords. The analysis results showed that studies on the utilization of AI technology for language learning have gradually increased in number and grabbed considerable attention among scholars in the Asia context. Several mainstream key terms attached to AI technology comprised personalized learning, mobile learning, and chatbot applications, indicating more concerns in reviewing the role of AI technology as a smart personal assistant for language learners. Furthermore, the use of AI technology was found to be beneficial for maximizing language learning preparation, language skills development such as reading and writing, and language learning evaluation particularly in providing feedback or assessing students’ works. However, challenges in using AI technology in a language learning context remain on the surface. The present mapping analysis can serve as a reference for contemplating the retrospect and envisioning the prospect of AI-powered technology use toward sustaining advanced and quality language learning.Downloads
Downloads
Published
2024-01-25
How to Cite
Arif Husein Lubis, Didin Samsudin, Risa Triarisanti, Mohammad Iqbal Jerusalem, & Yoonjung Hwang. (2024). A Bibliometric Mapping Analysis of Publications on the Utilization of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Language Learning. Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology, 38(1), 156–176. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.38.1.156176
Issue
Section
Articles




























