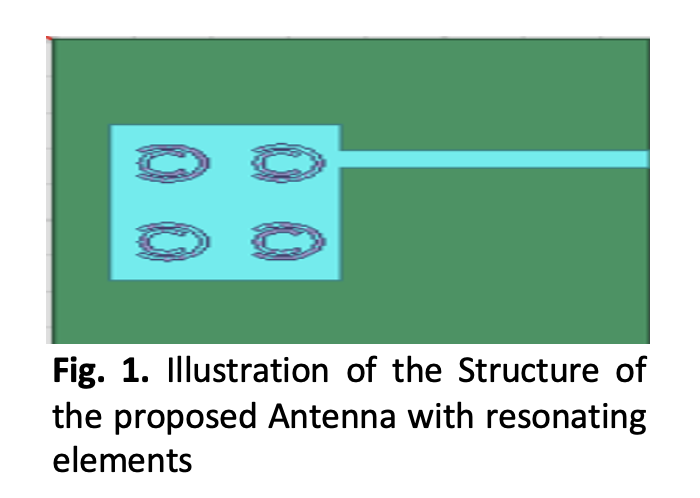
Investigation of Split Ring Resonator Based Rectangular Micro-Strip Patch Antenna for Radar Communication
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.1.171178Keywords:
X band, split ring resonators, radiation pattern, gain, voltage standing wave ratio, HFSSAbstract
The advent of antenna technology has greatly influenced the field of wireless communication. In this paper, a novel rectangular microstrip patch antenna with split ring resonators is presented. It is intended for use in the X-band, which normally operates between 8 and 12 GHz. Split ring resonators are incorporated into the radiating patch to increase gain and frequency bandwidth. Based on Rogers TMM 10TM, a dielectric material with a relative permittivity of 9.8, the antenna is made to operate at 10.4 GHz in the X-band. Several factors, such as S-parameters, radiation pattern, Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR), gain, and directivity are used to assess the performance of the proposed antenna. The design and simulation of the antenna need the usage of High-Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) software. The findings imply that the suggested antenna configuration has an efficiency of 93.5% and is proved to be an excellent candidate for Radar Communication because of its wide frequency bandwidth and other performances.
Downloads