A Comprehensive Study on EDFA Gain Flattening for WDM Transmission using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.40.1.96108Keywords:
Gain flattening , Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA), Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs), Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), Noise Figure (NF)Abstract
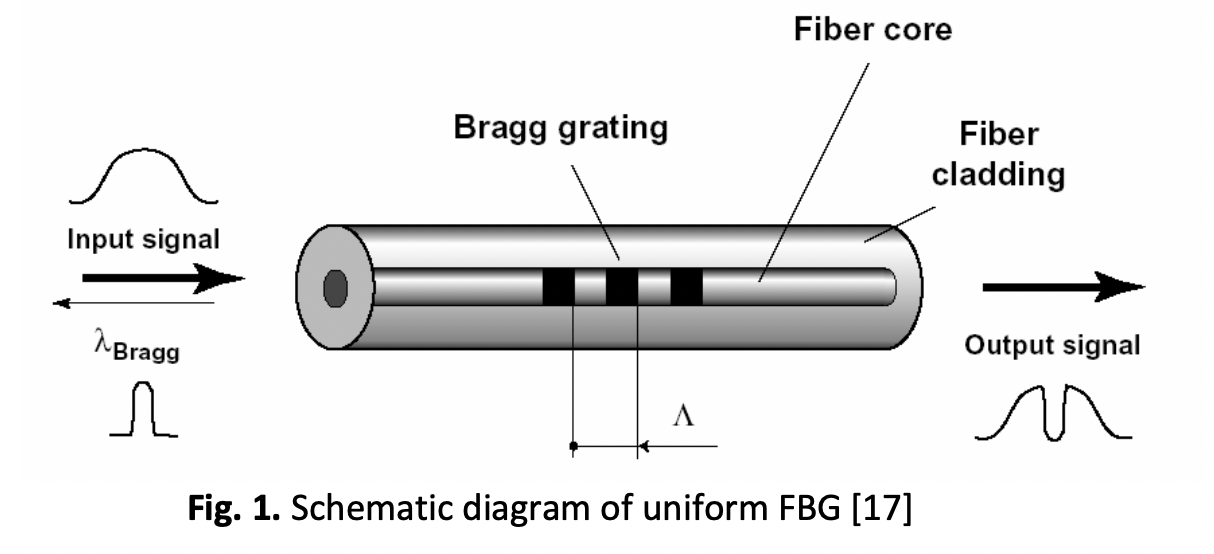
The gain flattening of optical amplifiers plays a crucial role in optical Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) communication systems, ensuring uniform amplification across all channels. This study focuses on investigating the gain flattening characteristics of Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) using cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBGs) in the C-band wavelength range. A comparative analysis of various optical amplifiers revealed that EDFA exhibited the highest gain variation, making it an optimal choice for gain flattening. The key parameters to achieve optimal EDFA gain flattening include the wavelengths of the channels, EDFA length, noise figure (NF), and the number of cascaded FBGs. Simulation experiments are conducted using Optisystem software (ver. 14.2) and the obtained results reveal that EDFA gain flatness can be achieved within the wavelength range of 1531 to 1533 nm, utilizing an EDFA length of 6 m and 12 cascaded FBGs. These findings contribute to the advancement of gain flattening techniques in optical WDM systems, enhancing their performance and reliability.
Downloads