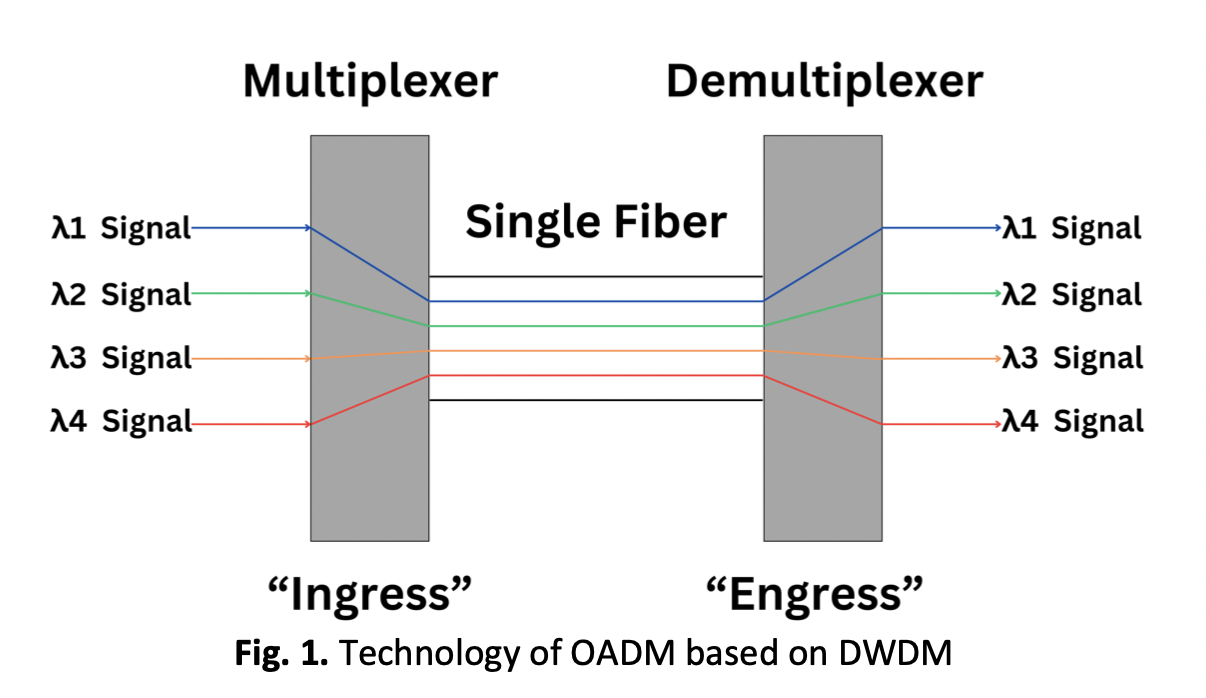
Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers: Enhancing High Transmission Bit Rates in Next-Generation Communication Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.43.1.251262Keywords:
Optical add-drop multiplexers (OADM), Dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM), Artificial neural networks (ANNs), High-speed optical networksAbstract
The development of optical networks in the telecommunications sector is becoming much closer by considering the help of an Optical Add Drop Multiplexer (OADM) based on a novel technology called Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM). The objective of the current study to examine high transmission bit rates for next-generation optical communication networks using the technology of OADM Based on DWDM. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were developed via MATLAB software to predict three main parameters in this filed such as transmitted signal power (PT), transmitted signal bandwidth (B.Wsig), and transmission bit rate capacity (Bsh) at different fiber cable lengths, such as L=200, 250, and 300 km. The ANNs results showed that, standard error (SE) for predicting PT as a function of the number of transmitted channels (Nch) was 0.115 mW, 0.095 mW and 0.077 mW, for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. Additionally, the SE for predicting B.Wsig was 0.067 GHz, 0.051 GHz and 0.040 GHz for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. Lastly, the SE for predicting Bsh was 1.665, 1.311 Gbit/sec and 1.076Gbit/sec for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. The SE for predicting PT as a function of the Signal Wavelength (λ) was 0.116, 0.096 and 0.079 mW for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. Additionally, the SE for predicting B.Wsig was 0.067, 0.052 and 0.052 GHz for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. Lastly, the SE for predicting Bsh was 1.688, 1.417 and 1.110 Gbit/sec for 200, 250 and 300 km, respectively. The low SE in ANNs demonstrated the efficiency, motivating further advancements in optimizing network performance for high-bit-rate transmission.
Downloads