A Consistent Augmented Stacking Polynomial Optimized Tool (ASPOT) for Improving Security of Cloud-IoT Systems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.1.1636Keywords:
Cloud, Internet of Things (IoT), Security, Intrusion detection system (IDS), Deep learning, Augmented stacking polynomial optimized tool (ASPOT), Binary sand cat swarm optimization (BSCSO)Abstract
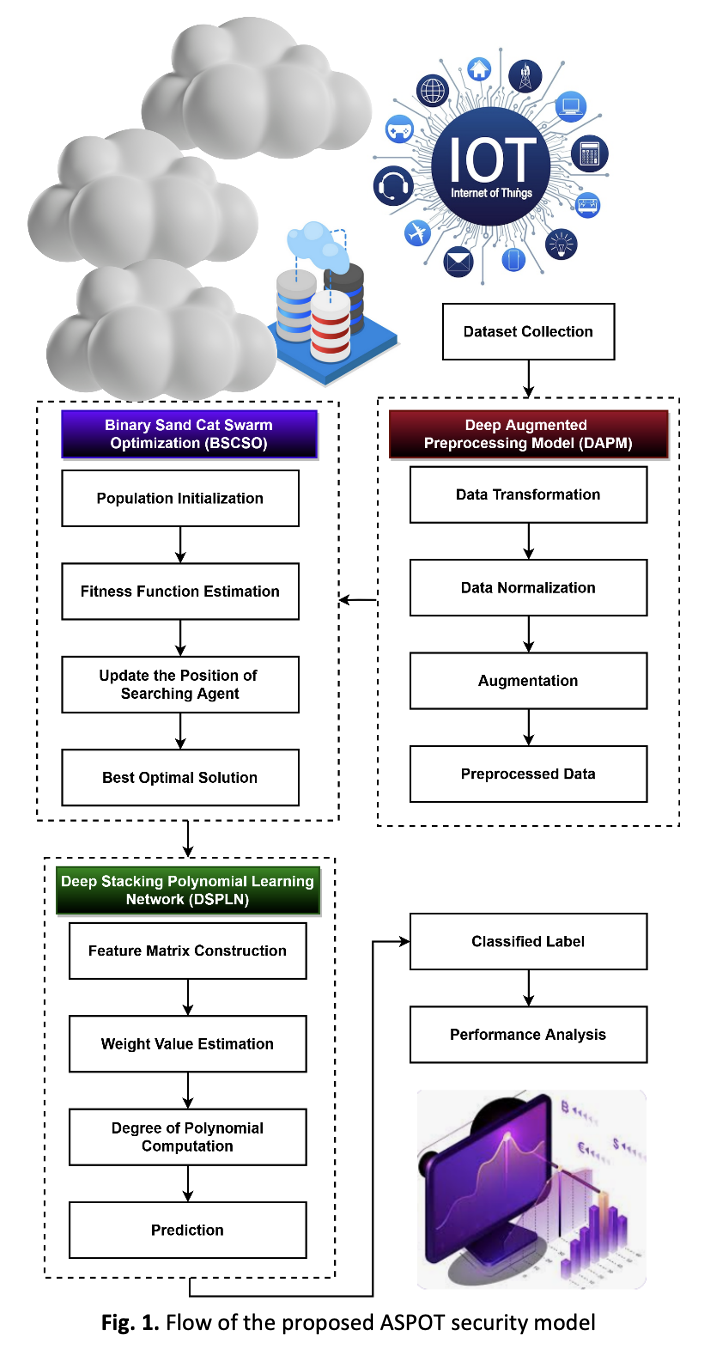
The cloud computing transforms information technology by offering end users simulated, flexible resources on demand that require fewer resources and facilities giving them greater flexibility. These materials are delivered over the Internet using predefined networking protocols, regulations, and styles, and they are overseen by various management groups. There are flaws and vulnerabilities in the underlying technology and legacy protocols that could allow an attacker to get access. A recent assessment of the literature led to the conclusion that most intelligence algorithms have a number of complex issues, including a high false prediction rate, difficulty classifying threats, high processing costs, and system load. Hence, the proposed work aims to develop an innovative and lightweight Augmented Stacking Polynomial Optimized Tool (ASPOT) for strengthening the cloud-IoT system security against modern cyberattacks with a accuracy of 99%. The current study uses the lightweight Deep Augmented Preprocessing Model (DAPM) to clean and normalize the input cyber-attack dataset by executing transformation and normalization operations on it. Furthermore, the Binary Sand Cat Swarm Optimization (BSCSO) technique is utilized to identify the most significant and relevant features of the normalized dataset in an optimal manner. Moreover, the class of assaults is promptly and precisely identified from the given data by applying the Deep Stacking Polynomial Learning Network (DSPLN) technology. The effectiveness and results of the proposed ASPOT method are analysed with the use of current cyber-attack statistics and a variety of assessment metrics.