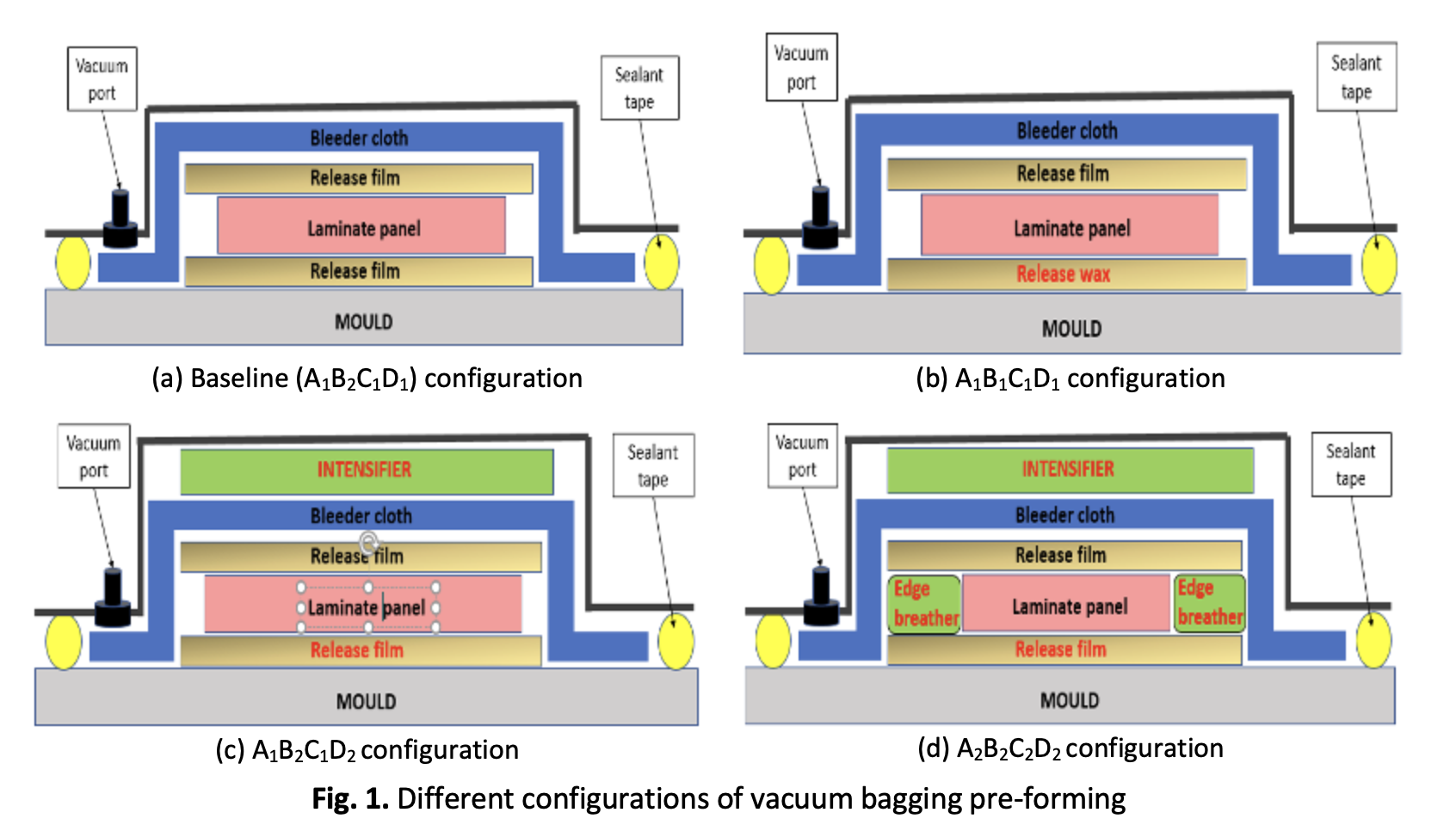
Significant Effect of Vacuum Bagging Processing on Inter-Laminar Shear Strength and Voids of Composite in Oven Cure
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.1.6981Keywords:
Interlaminar stresses, Shear strength, Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Process optimizations, Voids, LaminateAbstract
Autoclave had been constrained to longer time consumption, higher production costs and excessive residual stress. The challenges regarding with out-of-autoclave (OOA) cure involved the need to devise the techniques in preserving high quality of composite product during service life. The current work was proposed to quantify the impact and influence of pre-forming parameter variations in vacuum-bagging-only with oven curing (VBO-oven cure) of OOA manufacturing composite processing on the inter-laminar shear strength (ILSS) of low-cost conventional composite laminates. The relationship of ILSS and void quality characteristics was also investigated. Series of conventional lower-cost glass/epoxy aerospace-grade material was fabricated using 16 different processing routes in conventional oven. Burn-off and ILSS test was conducted based on ASTM standard to compute the ILSS and void content of cured laminates. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed on the post-test ILSS coupons to evaluate the relationship between void characteristics and ILSS. Results indicated that mould release type and intensifier contributed highest effects towards ILSS of approximately 31.3% and 27.6%, respectively. The assessment of ILSS-void relationship was further carried out and it was found that void geometry has a greater influence towards ILSS than the void content of composite laminate. The combination of these factors in processing routes yielded the lowest ILSS and void content at 24.85 MPa and 5.74%, respectively. These concluded that an optimized manufacturing technique could be expanded from the optimum settings of these processing parameters.