The Optimization of Vacuum-Bagging Processing in Oven Cure for Tensile Strength in Composite Laminate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.37.1.3748Keywords:
Composite, Manufacturing optimization, Tensile, VBO-oven cure, Out-of-AutoclaveAbstract
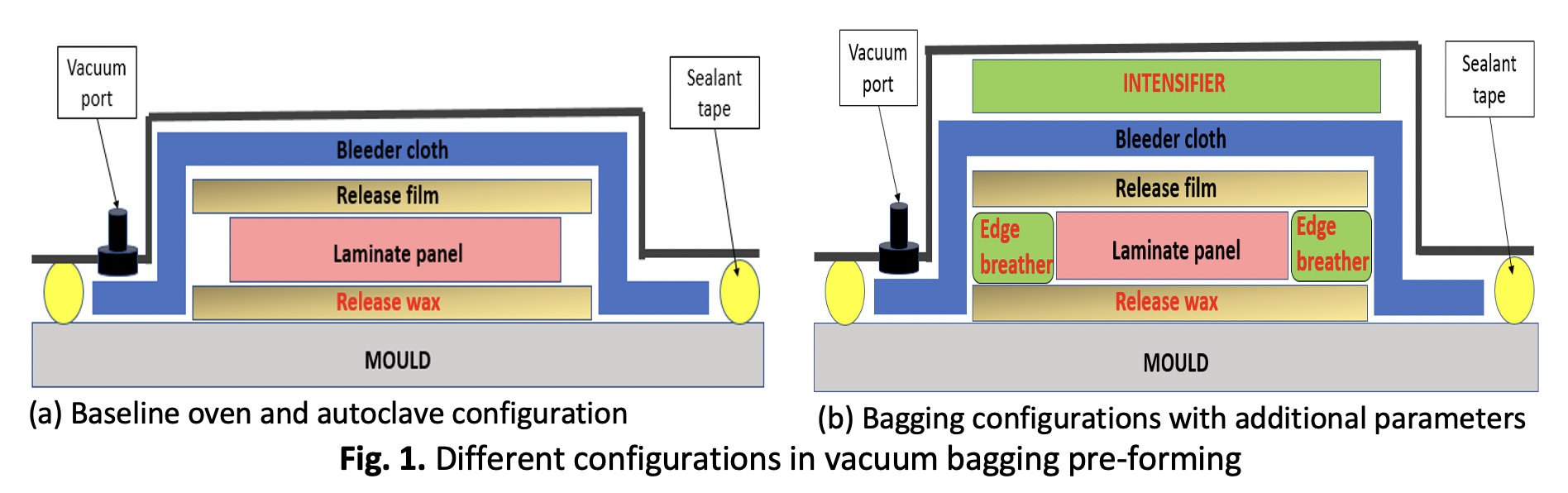
The implementation of autoclaves has been limited due to high production costs and an excess of residual stress. These drawbacks have led to the exploration and development of an alternative method known as out-of-autoclave (OoA) manufacturing process. This research study was proposed to enhance the production of high tensile strength in composite laminate by optimizing the vacuum-bagging-only (VBO) pre-forming process. The impacts of both individual and combined pre-forming parameters in VBO-oven cure processing were measured for traditional low-cost glass/epoxy composite material with respect to the tensile strength of the cured laminates. Twenty composite panels were produced according to specified parameter combinations using central composite design in a fractional factorial approach for creating a response surface model. The study examined three variables, namely the duration of vacuum debulking, the number of sides with edge breather, and the weight of the intensifier. Two laminates were manufactured without additional processing parameters using both the oven (baseline) and autoclave methods for validation purpose. Subsequently, a tensile test was carried out following ASTM D 3039. The interaction among the combined parameters was examined using analysis of variance (ANOVA). The laminates exhibited the lowest tensile strength when the intensifier was not present, while the highest tensile strength was recorded when edge breather, debulk, and intensifier were applied at varying levels. An ideal processing configuration of 30 minute-debulk, each side of edge breather and 1kg-intensifier had resulted in the production of laminate with the highest tensile strength, measuring 407.44 MPa. This value was roughly 17.2% higher than that of the baseline laminate and 3.77% higher than the autoclave laminate.
Downloads