Tribological Characterisation of Biofluid using Four Ball Experiment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.65.1.122137Keywords:
Four ball, sunflower oil, olive oil, artificial synovial fluid, hyaluronic acidAbstract
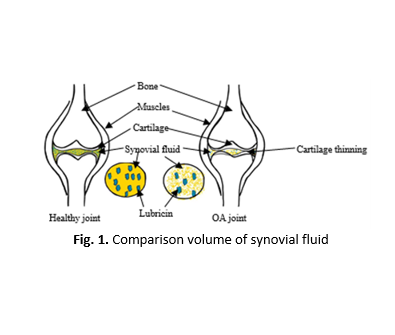
This project study about the tribological characterisation of biofluid that used plant-based oil which namely sunflower oil and olive oil that been blends with hyaluronic acid as an additive. Plant-based oil is a type fluid that not be harmful to human and the hyaluronic acid helps the based fluid in absorption shock and distribution of forces. This project aims to measure the performance of this biofluid acts as an artificial synovial fluid in term of its coefficient of friction, frictional torque and the wear scar diameter produced. There are three different composition volumes of hyaluronic acid going to be used which are 0%, 5% and 10% in the fluid sample. This sample of biofluid going to be tested by using four ball tribological testing under one of the conditions which was wear preventive condition to obtain the coefficient of friction and frictional torque for the biofluid while by using the 3D Surface Measurement Systems was to measure the wear scar diameter produced at the ball bearings. The result that been acquired for this study which are the average coefficient of friction and frictional torque were directly proportional to the volume composition of additives. However, for the average wear scar diameter, it depends on the suitability of volume additives been added. Pure Sunflower oil has lowest coefficient of friction which is 0.065940. While, for average wear scar diameter, Olive oil with 10% hyaluronic acid recorded the lowest value which is 0.64828mm. It shows that pure plant-based oil having the best lubricant ability which is producing lower coefficient of friction and frictional torque compared to it going to be blend with hyaluronic acid. This result of this project might give benefits to the medical engineering nowadays that related to the case that need the usage of artificial synovial fluid.
Downloads