Edge Enhancement and Detection Approach on Cervical Cytology Images
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.28.1.4455Keywords:
Edge Detection, Nucleus, Cytology imageAbstract
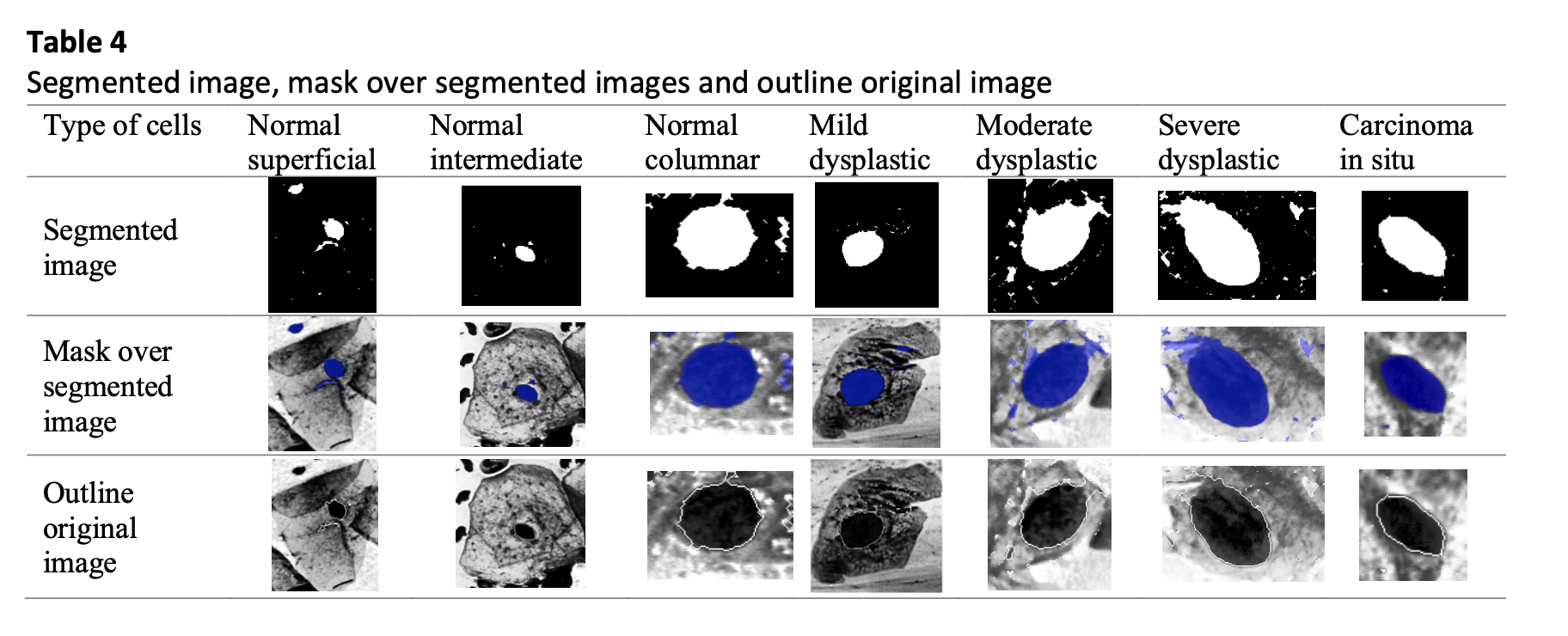
Cervical cancer is a prevalent and fatal disease that affects women all over the world. This affects roughly 0.5 million women annually and kills over 0.3 million people. Recently, a significant amount of literature has emerged around the advancement of technologies for identifying cervical cancer cells in women. Previously, diagnosing cervical cancer was done manually, which could lead to false positives or negatives. The best way of interpreting Pap smear images and automatically diagnose cervical cancer are still up for debate among the researchers. Method used in this study is the contrast enhancement technique for pre-processing and edge detection-based for segmentation of the nucleus. In this study, the average performance results of the method showed an accuracy of 96.99% in the seven-class problem using Herlev dataset. The present finding also support this study which concluded the results of accuracy achieved for the algorithm used for nucleus detection is improved by 6.15% when comparing to previous work. The accuracy value is in the lines of earlier literature that achieved accuracy of the approach used above 90% for seven class of cells. The major feature of the suggested approach is an improvement in the ability to anticipate which cells are aberrant and which are normal. Adding more classifiers could improve the suggested system even further. Therefore, a cervical cancer screening system might utilize this framework to identify women who have precancerous lesions.
Downloads