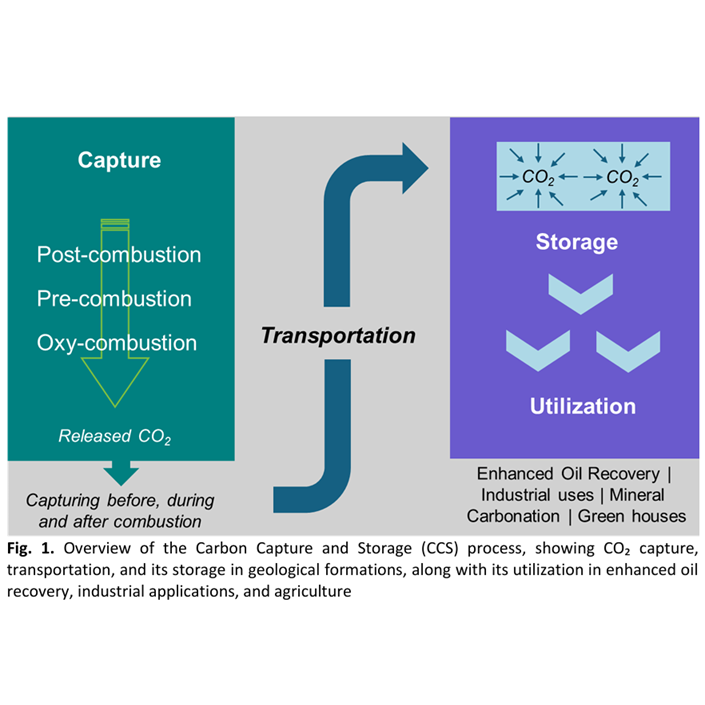
Optimizing Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) through Thermal Biomass Conversion into Terra Preta and Hydrogen: A Short Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.126.2.1325Keywords:
Carbon capture and storage (CCS), thermal biomass, terra preta, hydrogenAbstract
Mitigating climate change and implementing sustainable agricultural practices represent vital global challenges. Innovative solutions like Terra Preta, a biochar-enriched soil amendment, present promising methods to enhance soil health, augment agricultural productivity, and sequester carbon. This review seeks to assess the advancement and optimization of a Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) framework that transforms thermal biomass into Terra Preta and hydrogen, a sustainable energy byproduct. The review involves an examination of CCS technologies, the thermal conversion of biomass, and the prospective advantages of Terra Preta for agriculture and carbon sequestration. The paper outlines experimental design factors for enhancing Terra Preta production and evaluating its impact on agricultural systems. Key findings show that Terra Preta can significantly enhance soil fertility, augment crop yields, and foster resilience to environmental stressors while sequestering carbon. However, long-term field studies are necessary to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of Terra Preta across various agricultural systems and climates. These insights allow the continuous advancement of this innovative technique, which possesses the capacity to enhance sustainable agriculture and mitigate climate change. Subsequent research needs to be focused on enhancing production methodologies, investigating the enduring effects of Terra Preta on soil vitality, and analyzing its contribution to the mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions. Funding proposals for additional research and development will be guided by the findings presented in this review.
Downloads