The Effect of Linear, Parabolic and Inverted Parabolic Salinity Gradients on The Onset of Darcy Brinkman Rayleigh Benard Two-Component Convection in a Two-Layered System with Dufour Effect
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.101.2.121136Keywords:
Dufour effect, two component convection, Rayleigh number, composite layerAbstract
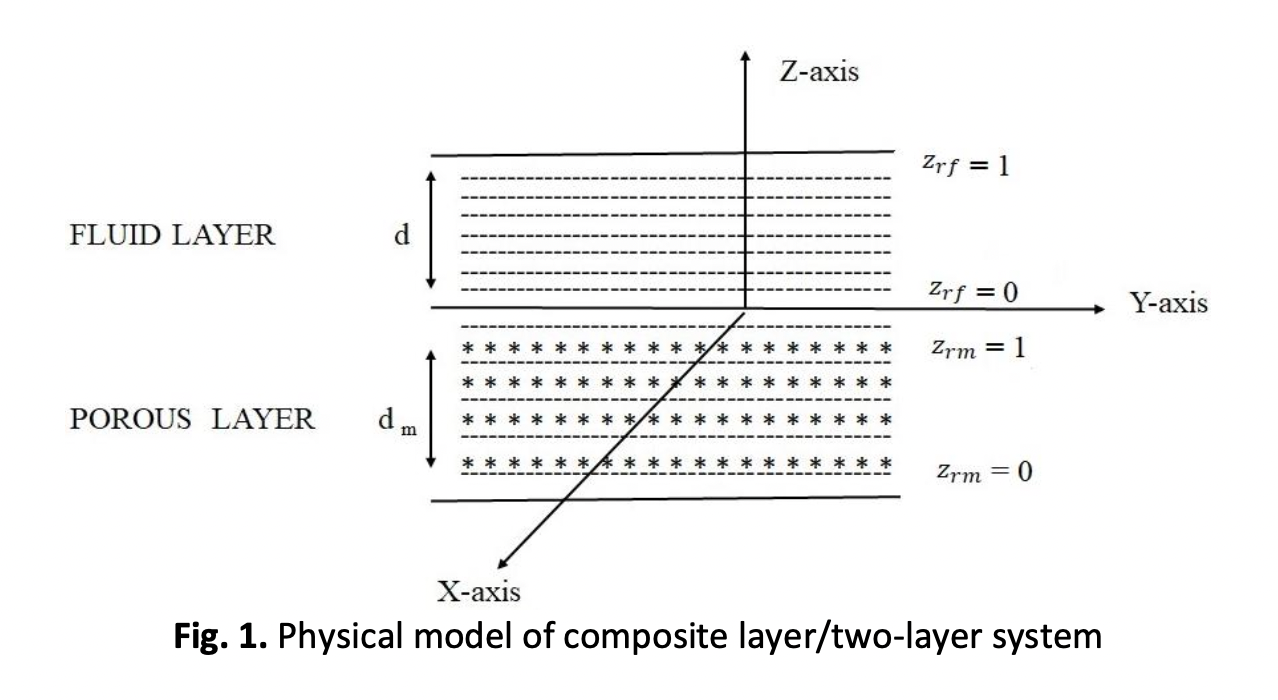
The physical configuration of the problem of Darcy Brinkman (DB) Rayleigh Benard Two-Component (RBTC) Convection in a two-layered system has been investigated for linear, parabolic and inverted parabolic salinity gradients with the Dufour effect. For the fluid layer, the upper boundary is free with surface tension and for the porous layer, the lower boundary is rigid. At the interface, the normal velocity, normal stress, shear stress, mass, mass flux, heat, and heat flux are continuous. The regular perturbation method is used to solve the resulting ordinary differential equations obtained from normal mode expansion. The effect of different physical parameters on the Rayleigh number versus depth ratio is discussed and results are presented graphically.
Downloads