Numerical Investigation on Thermal and Electrical Stress in Electric Vehicle Cabling Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.1.2536Keywords:
Electric vehicles, components, wiring harness, cabling network, thermal stress, electrical stress, finite difference methodAbstract
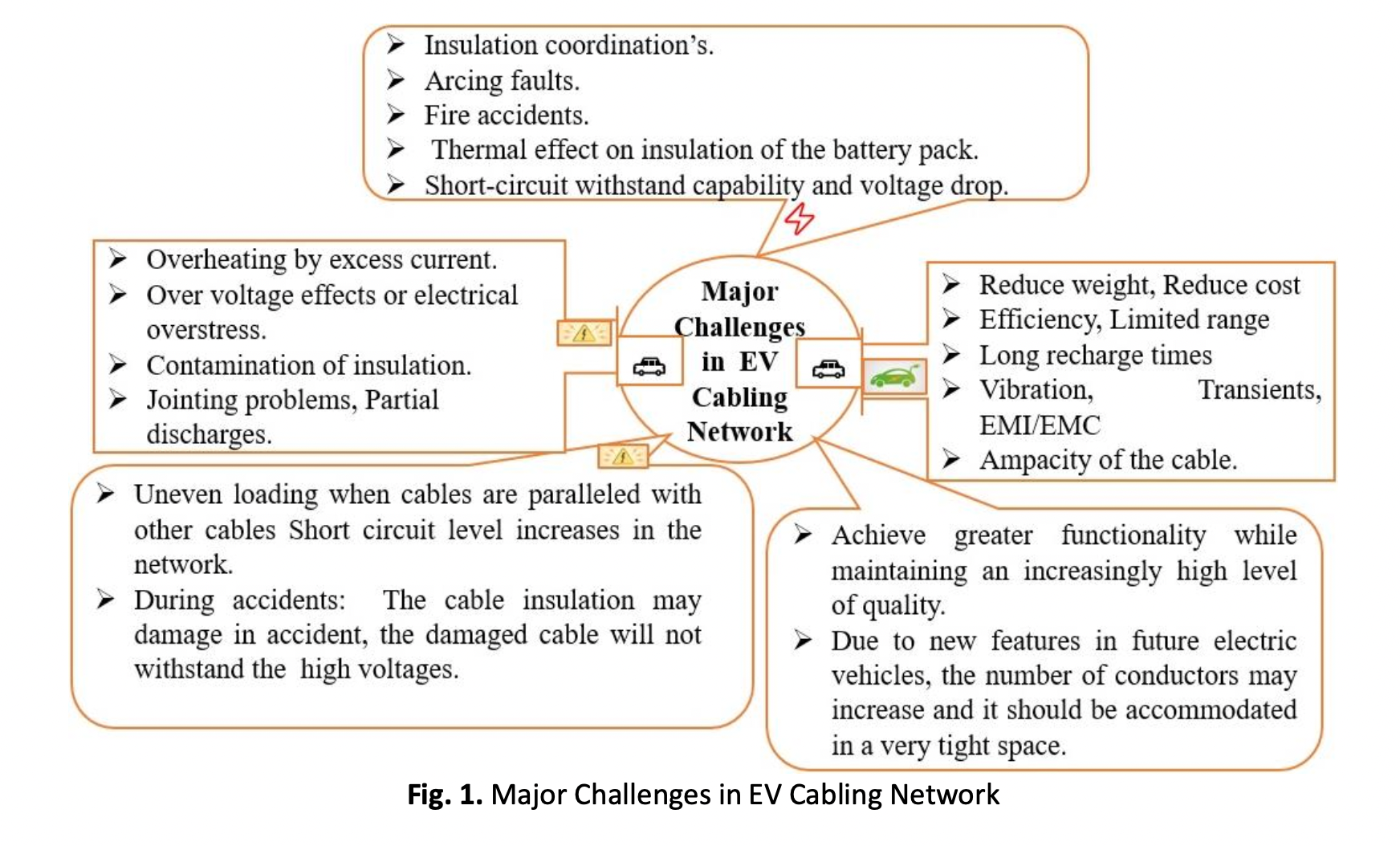
Global warming and an impending energy problem have compelled nations to become greener and cleaner. Worldwide, interest in electric vehicles (EVs) is growing as a result of rising gasoline prices and environmental concerns. The need for electrical components and cabling networks is expanding along with the demand for electrified vehicles. The complexity of vehicle electrical, electronics, and control circuits is also rising. There are many wire and cable performance issues in modern e-mobility, including limited space, vibration, high-temperature variation, unfriendly fluids, and rising data transmission requirements. Thus, it is important to study and evaluate the thermal and electrical stresses in the electric vehicles cabling network to avoid insulation failure, which causes fire accidents in the electric components of EVs. An EV's entire electrical system gets hotter, and insulation strength is affected by both temperature and the electrical field. The insulation system is one of the most important components in any electrified vehicle. From a design and protection perspective, the computation of electric potential distribution and electric field within and around the cables of electric vehicles is very important. The strong non-linear dependency of the electrical conductivity of the insulation material on prevailing electrical stress and temperature makes the field problem not only coupled but also non-linear. Finite Difference Numerical (FDM) is used for non-linear field computation. In this paper, different electric vehicle cabling network layouts were studied and listed the challenges. Chosen the high voltage cables of electric vehicles from the cabling network and numerically computed the conductivity, temperature, and electrical fields of cable.
Downloads