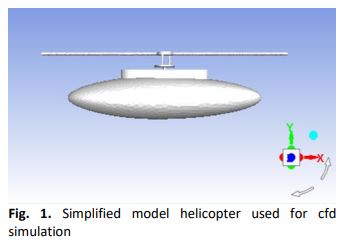
Static Analysis of Unsteady Aerodynamics Wake of Simplified Helicopter Model Via Simulation Work
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.89.1.142153Keywords:
Static analysis, turbulence model, computational fluid dynamics, unsteady wake, simplified modelAbstract
Computational tools have led and helped researchers in providing advanced results, notably in rotorcraft research, as flow around the helicopter is dominated by complex aerodynamics and flow interaction phenomena. This research work aimed to evaluate the aerodynamic computational results on a simplified model helicopter when the model was subjected to the angles of attack 0°, -5°, -15°, and -20°, respectively. The study also examined the unsteady flow behaviour on the three-dimensional elliptical shape of a fuselage equipped with a rotor hub of the single rotor blade. The computational domain for the aerodynamic flow field was created within the size of 7 m (length) x 5 m (width) x 5 m (height). Results showed that an increase in the angle of attack in the rotor component caused additional drag of about 34% to 45% whilst the fuselage component contributed about 55% to 65% to drag increment. Also, a significant value of total pressure from -235 Pa to 250 Pa demonstrated along the simplified model helicopter distinctly showed that the complexity of geometry caused adverse pressure. The findings of this research work could potentially improve the understanding of complex flow surrounding the helicopter that has always baffled the aerodynamicists.
Downloads