Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Thermal Behavior of Alumina-Water Nanofluid Inside Hexagonal and Octagonal Enclosed Domain
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.103.1.4063Keywords:
Hexagonal, octagonal, three dimensional, cavity, nanofluidAbstract
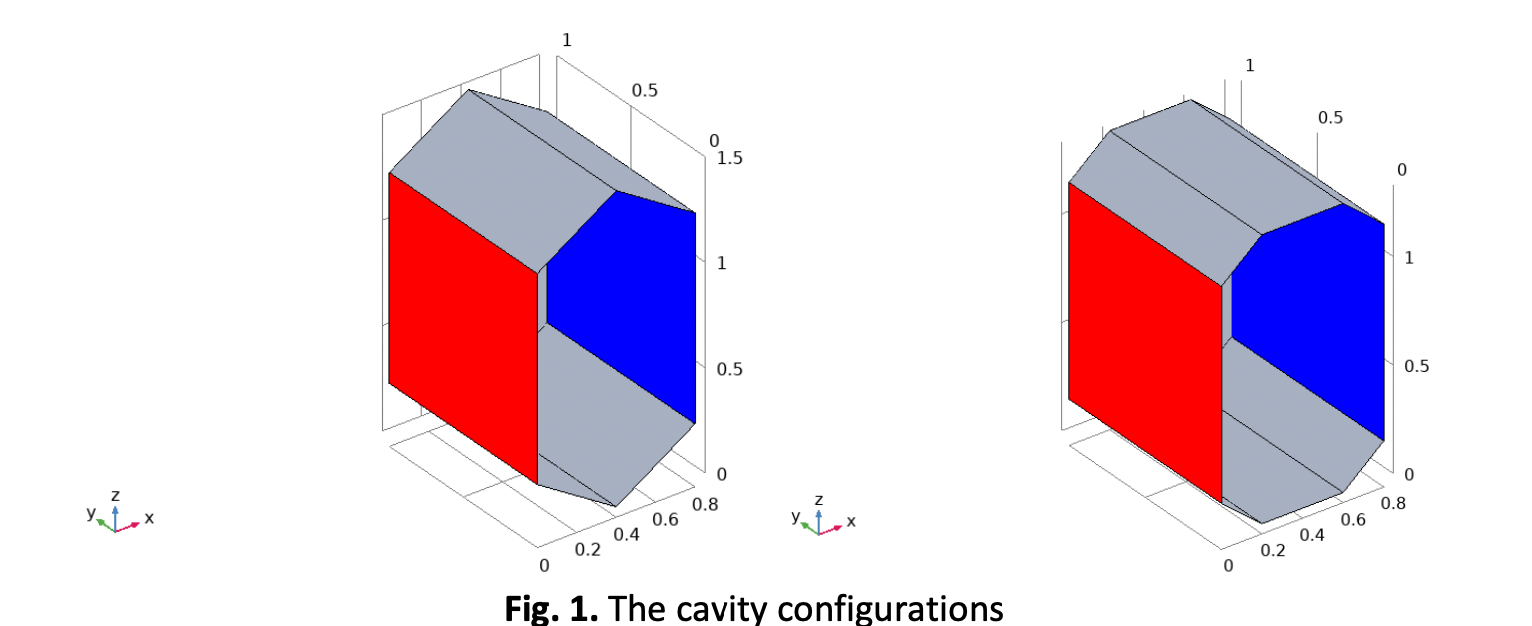
The current work focused on the study of the laminar and steady free convection of Aluminum Oxide / Water nanofluid inside cavities. Two different cavities have the same volume but different overall surface area and count of walls are studied. These cavities are heated differentially on the vertical square side walls which of identical area and dimensions for both cavities. The other vertical walls of these cavities have hexagonal and octagonal shapes. The first cavity has eight walls while the second has ten walls. The study accomplished for solid particles volume fraction and Rayleigh number ranges of (φ = 0.01, 0.03, 0.05) and (103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106). The study interested highly by the effect of the cavity geometry parameters including the lateral cross section, the height, the number of walls on the flow and heat transfer. Other flow parameters are recognized on the fluid flow and heat transfer fields like the nanoparticles volume fraction and the Rayleigh number. The results indicated that the surface area increase by means the additional walls has an observed effect on guiding the results. Where the octagonal cavity has better enhancement in heat transfer especially at (Ra=104 and 105). The percent increase in Nu over the hexagonal cavity is (0.6, 0.8, 0.7, 0.3) for the specified Ra range.
Downloads