Analysis of Wind Speed Prediction using Artificial Neural Network and Multiple Linear Regression Model using Tinyml on Esp32
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.107.1.2944Keywords:
Embedded system, TinyML, Multiple Linear Regression, ANN, wind speed prediction, ESP32, air qualityAbstract
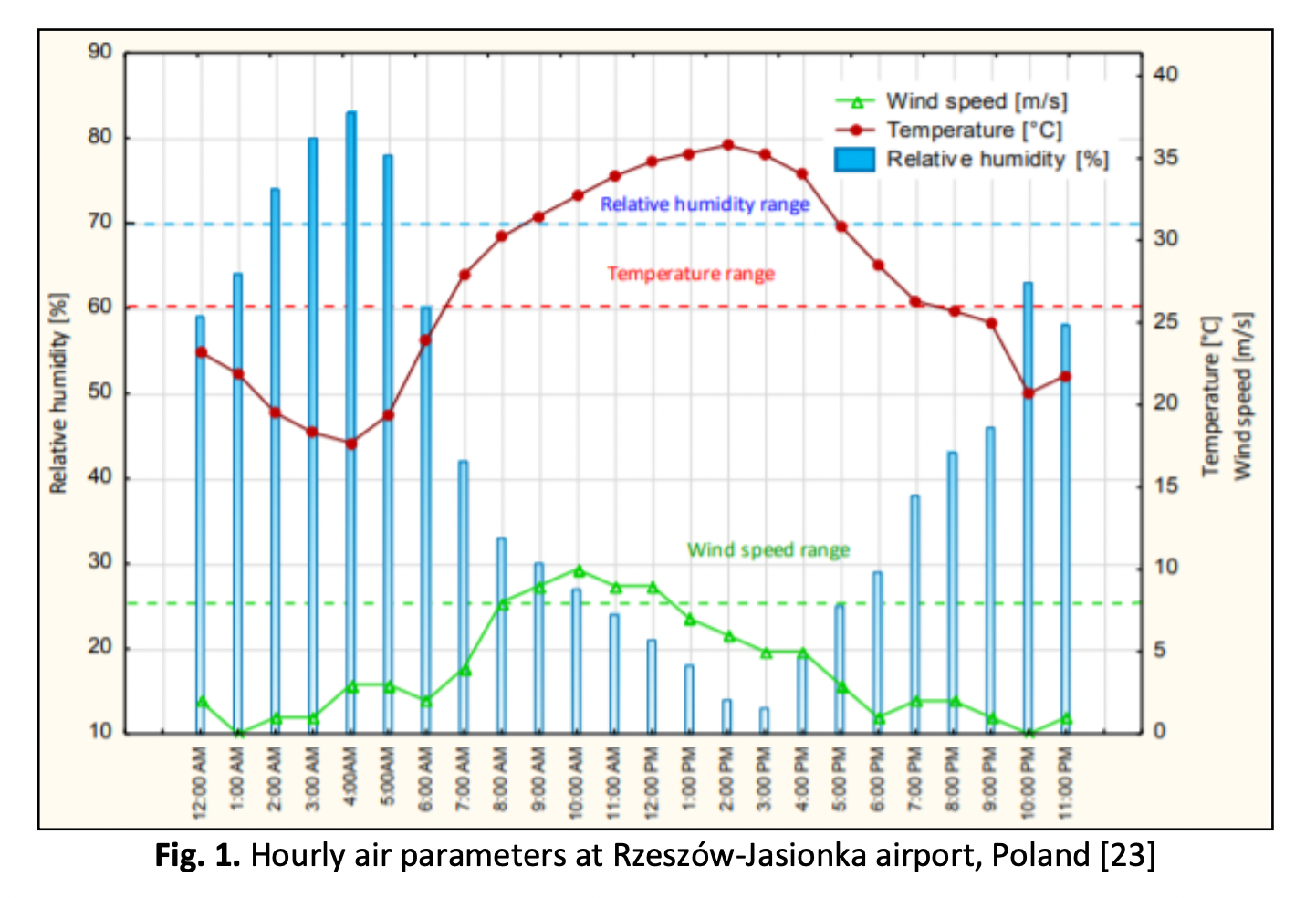
This study provides the investigation of wind speed forecasting using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Linear Regression Model with an ESP32 chip. A portable wind speed prediction system will aid in mitigating the risks associated with sudden gusts of wind by forecasting the maximum wind speed that may occur in the near future. This research also demonstrates the application of TinyML in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) by applying a Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model to small, low-powered ESP32 microcontrollers to analyse data with low latency. The system predicts wind speed in Setapak, Kuala Lumpur, based on the measured temperature and humidity using a DHT22 sensor and displays forecast results and sensor readings on LCD screens. To measure the accuracy of the MLR and ANN models, the coefficient of determination ( , mean square error (MSE), and root mean square error (RMSE) between predicted and actual results are evaluated. Results indicate that the ANN model outperforms the MLR model for predicting wind speed.
Downloads