Effect of GO Solution Temperature on the Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ZnO Nanostructured for Photoanode Function
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.102.2.99109Keywords:
Zinc oxide, graphene oxide, immersion temperature, electrical and nanostructuresAbstract
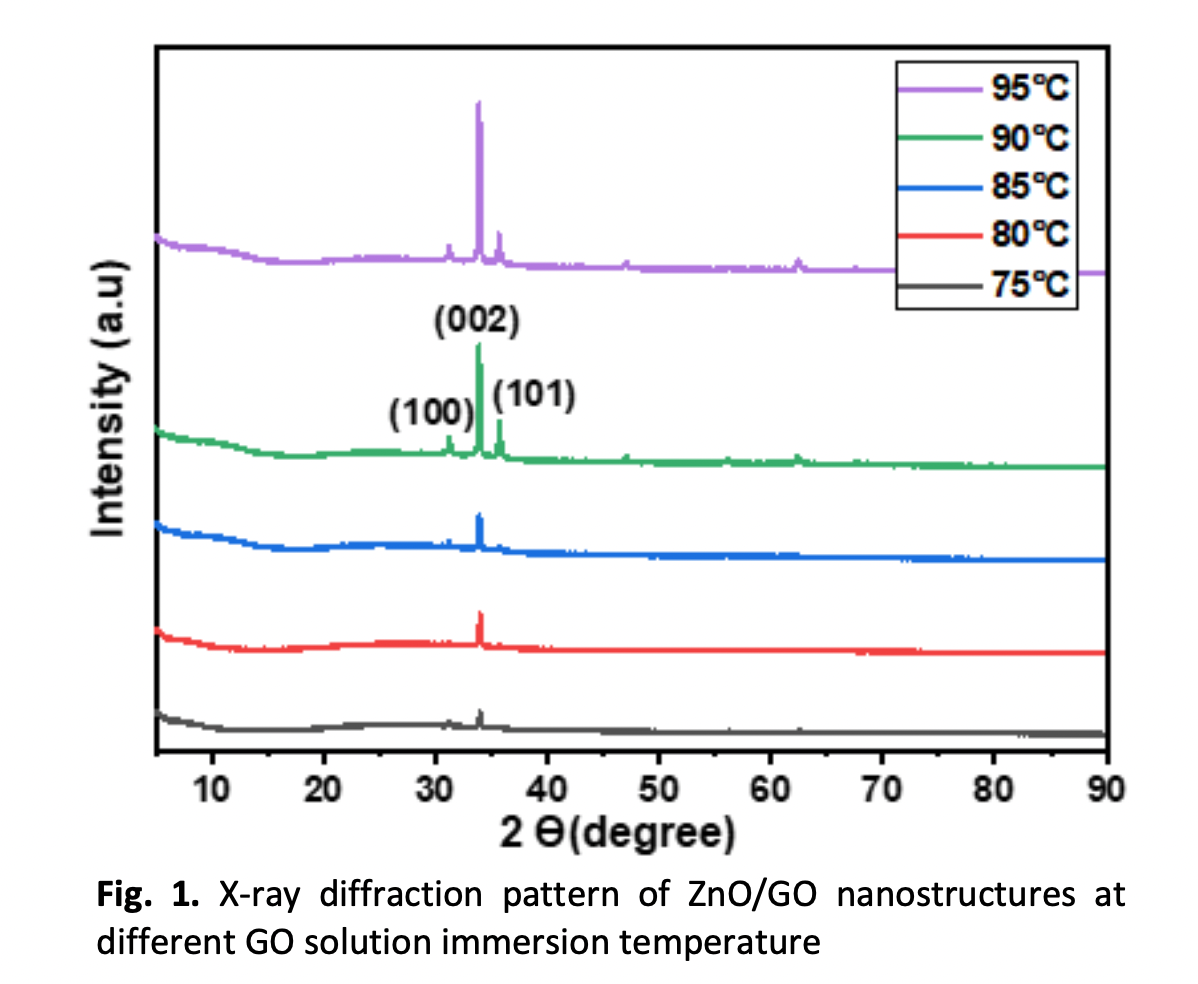
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of different graphene oxide (GO) solution immersion temperature on the structural, morphology, optical, and electrical properties of zinc oxide/graphene oxide (ZnO-GO) nanostructures. The ZnO/GO nanostructures prepared at various GO solution immersion temperature from 75-95℃ using solution immersion method. The structural properties of the samples were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the recorded patterns revealed that all the samples had a preferred orientation along the (002) plane. The crystallinity of ZnO/GO nanostructures were enhanced with increasing GO solution immersion temperature. The morphology of ZnO/GO nanostructures was determined using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to determine the molecular compounds of ZnO/GO nanostructures. The peak intensity of GO with ZnO nanoparticles is shifted at 744 to 1243 cm-1 when the temperature of GO solutions increases. The UV–visible spectrophotometer was used to examine the optical properties of ZnO/GO nanostructures. It is found that the highest transmittance ZnO/GO nanostructures was obtained at the highest GO solution immersion temperature which is 95℃. Based on the current-voltage(I–V) measurement, the electrical properties of ZnO/GO nanostructures increase when the GO solution immersion temperature increases. Thus, by variation of GO solution immersion temperature the structural, morphology, optical, and electrical behaviour were improved.
Downloads