Investigation of Dual-Pump Fiber Optical Parametric Amplifier Performance Driven by Energy Transfer Between Four-Wave Mixing Process
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.90.1.5263Keywords:
2p-FOPA, gain, higher-order dispersion, fiber parameters, pump parameters, energy transfer, FWMAbstract
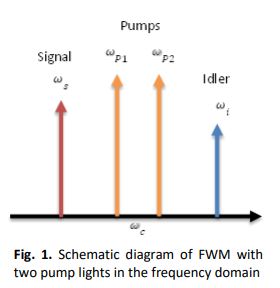
Fiber optical parametric amplifier (FOPA) is operated based on energy transfer from pump waves to signal wave and at the end of the fiber, an idler wave is generated. This process is called four-wave mixing (FWM). Even though effects of higher-order dispersion coefficients, fiber length, fiber nonlinearity, fiber attenuation, pump powers, pump wavelength separation and distance of central pump wavelength with ZDW on gain profiles have been examined by previous researchers, but on different fiber or numerically studied using the Optisys system, analytical model or different amplitude equations. Thus, in this study, the above-mentioned parameters on the gain performance of dual pump fiber optical parametric amplifier (FOPA) using highly nonlinear shifted fiber (HNL-DSF) as a medium will be numerically investigated using ode45 function in Matlab. The gain at a certain wavelength can be obtained by solving 4 coupled amplitude equations with fiber loss and pump depletion that govern the four-wave mixing (FWM) process of pumps, signal and idler waves. Simulations results indicate positive gives poor or no gain, meanwhile, an addition of to negative widens the bandwidth, but there is no significant effect with the addition of . Besides, an increase of fiber length, nonlinearity and pump powers improve gain performance, but an increase of fiber loss decays the gain amplitude. Increment of pump separation will enhance flatness of gain at wavelength far from central wavelength but results in an increase of gain reduction at the central wavelength. Lastly, must be positive, not too small and not bigger than 1.125nm to get a high, broader and lesser ripples gain.
Downloads