Energy Measurement and Potential Energy Conservation Measures in Five Healthcare Buildings in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arfmts.113.1.5766Keywords:
Building, energy, Building Energy IndexAbstract
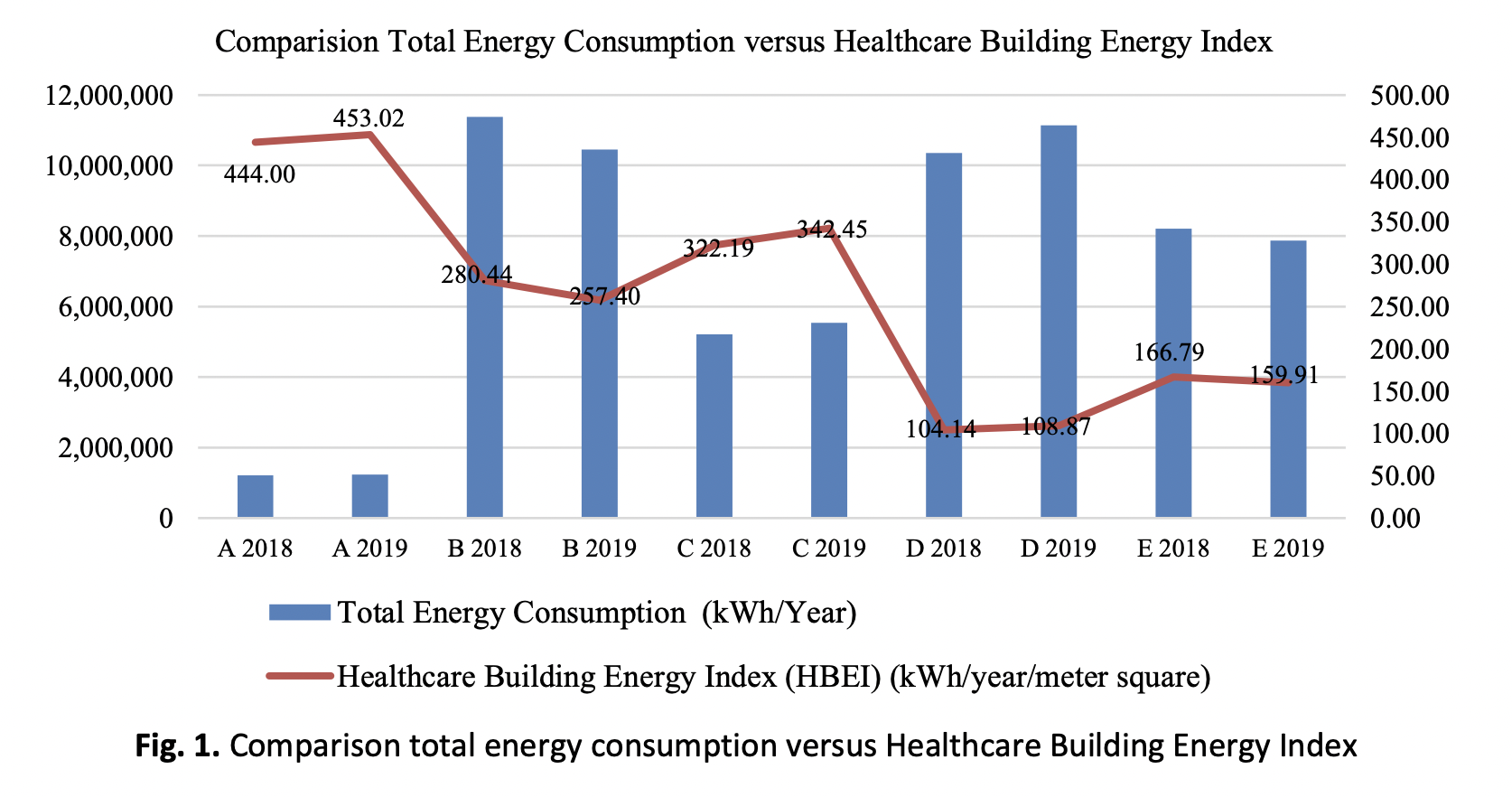
Concern is growing around the world as a result of the global economy's overall rise in carbon emissions and energy consumption. The healthcare facility is among the buildings in the world with the highest energy use. Thus, it is necessary to create energy-saving plans that evaluate the energy performance of buildings and put energy-saving measures into practice. Enhancing building energy efficiency is most commonly achieved through a comprehensive energy audit. The Building Energy Index is the current method used to analyses all forms of building energy performance. The operating hours of a healthcare facility are longer than those of a commercial building. The issue emerges when there is no clear criterion for establishing whether or not a healthcare facility is energy efficient, and the present norm may misread healthcare energy consumption. To determine the actual onsite energy use at the healthcare building, a full energy audit is performed. Five places are selected based on the sort of healthcare services offered. According to the on-site complete energy audit, cooling equipment consumes the most energy. The study's findings may be divided into two categories: Healthcare Building Energy Index from detailed energy audit results and derived directly from power bills for the years 2018 and 2019. In terms of Healthcare Building Energy Index, there is a contrast between utilizing detailed energy audit data and using utility bills directly. Nonetheless, a comparison of Healthcare Building Energy Index with existing Malaysian requirements reveals a significant discrepancy. Based on the audit and analysis results, several savings opportunities may be presented.
Downloads